The Essential Guide to Automating SEO Audits with AI - Choosing the Right SEO Audit Tool
Discover how to automate comprehensive SEO audits using AI-powered tools. Learn workflows, interpret findings, and integrate fixes for ongoing site optimization.
Posted by
Related reading
The Ultimate Guide to AI Powered SEO Content Strategy
Picture this. It’s Monday, 8:30 a.m., coffee in hand. You’re juggling 1,200 keywords in a spreadsheet, opening 11 tabs to compare SERPs, building briefs by hand, and begging teammates for internal link suggestions. By noon, you’ve written… a title. Now flip it. You upload those queries into an AI-orchestrated workflow. It clusters them by search intent, drafts a brief with entities to cover, surfaces internal link opportunities, and flags gaps against competitors. By noon, you’re editing a strong draft and planning the next cluster.
How to Choose the Best AI SEO Tools for Your Content Workflow
Atlas Content had the right people. Smart strategists, solid writers, a reliable dev. But their SEO workflow was stuck in the past. They were juggling keyword research in spreadsheets, copying SERP data into briefs, and manually grading content against competitors. Technical checks lived in a separate crawler export. Monthly reporting took three days and stole time from strategy. Sound familiar?
Streamlining Your SEO Workflow with All-in-One AI Tools
You know the drill. Five tabs open for keyword research, a spreadsheet for mapping topics, a separate crawler, a content editor plugin, and a reporting deck that takes half a day to update. By Friday, you’ve spent more time stitching tools together than actually moving rankings.
The Essential Guide to Automating SEO Audits with AI
You know the rhythm: spreadsheets sprawl, tabs multiply, and the clock keeps counting while you try to tame a site’s technical, on-page, and content issues. A modern seo audit tool changes that tempo by translating crawl chaos into clear, prioritized actions—automatically. With seo automation, you can move from periodic, error-prone sweeps to continuous visibility and faster fixes, guided by AI that spots patterns a human might miss. This guide shows you exactly how to set up, interpret, and operationalize AI-powered audits so you maintain momentum, not just a momentary snapshot of “site health.”
Why Automate SEO Audits? The Case for AI-Driven Optimization [#why-automate]
Manual audits vs. automation: what’s broken [#manual-vs-automation]
Manual audits have noble intentions but narrow lanes. They consume time, invite inconsistency, and often leave blind spots that surface only after rankings wobble or conversions slide. Even skilled teams struggle to maintain cadence across complex sites, where templates multiply and change logs are busy.
- Time cost: repeated crawling, copying, and reconciling across URLs, templates, and environments.
- Inconsistency: changing checklists, variable judgment calls, and drifting priorities from sprint to sprint.
- Blind spots: missed regressions between audits; late discovery of indexation errors, redirect loops, or JavaScript rendering failures. This friction isn’t a talent problem—it’s a tooling problem. Humans excel at judgment and strategy; machines excel at repetition and pattern detection. When you let automation handle the heavy lifting, you scale precision without trading away nuance.
How AI amplifies your process [#how-ai-amplifies]
AI turns your audit from a snapshot into a system. By blending machine learning, semantic analysis, and scheduled checks, ai seo tools surface what matters and suppress the noise. They help you detect subtle shifts in site structure, content duplication, and performance anomalies before they become ranking headwinds.
- Pattern recognition: identify canonical conflicts, template-level noindex, semantic duplicates, and recurring 3xx chains across clusters—not just single URLs.
- Anomaly detection: flag unexpected spikes in 5xx errors, CLS regressions, or index coverage drops with confidence indicators.
- Prioritization: rank issues by predicted impact and effort so your team tackles the highest-value fixes first.
- Continuous checks: monitor changes as they happen; confirm that fixes stick through automatic re-crawls and regression guards. The result is not merely “more data,” but context-aware, impact-weighted recommendations. Your team spends less time hunting problems and more time solving them.
Before/After workflow snapshot [#before-after-workflow]
Before: A marketer runs a manual crawl before a release, exports CSVs, and highlights issues in a spreadsheet. Hours pass triaging mixed-severity items. A week later, traffic dips—turns out a noindex tag slipped into a key template after the audit was done.
After: An AI-powered automated site audit runs on a schedule and reacts to changes. It detects a spike in noindex across a product cluster, labels it Critical, estimates risk to high-traffic pages, and triggers an alert with a pre-filled task for engineering. A validation crawl runs post-fix to confirm recovery—no guesswork, no stale snapshots.
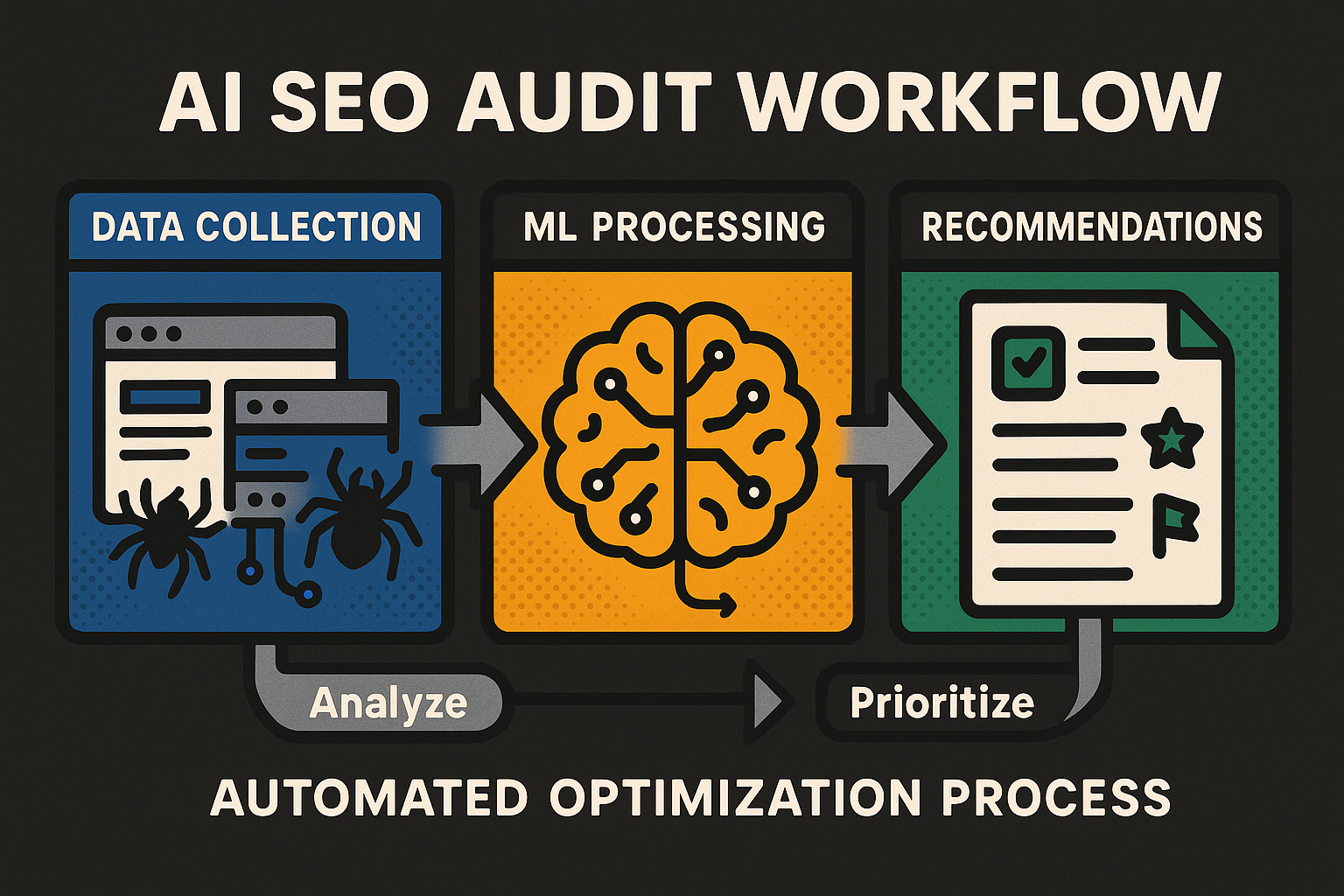
How AI-Powered SEO Audit Tools Work [#how-ai-tools-work]
Definition [#definition-ai-seo-audit]
An AI-powered SEO audit is an automated site assessment that uses machine learning and natural language processing to crawl pages, detect technical and on-page issues, and prioritize fixes by predicted impact. It turns raw crawl data into ranked recommendations so teams can resolve the highest-value issues first.
Compact glossary:
- Anomaly detection — automated identification of unusual changes (e.g., sudden noindex spikes, 5xx surges)
- Canonicalization — selecting the preferred URL to consolidate duplicates
- Core Web Vitals — user experience metrics such as LCP and CLS
- Crawl budget — how much of your site search engines are willing to crawl
- Semantic deduplication — grouping near-duplicate content by meaning, not just exact text
- Hreflang — signals language/region variants
- Index coverage — ratio of known or submitted URLs that are actually indexed
- JavaScript rendering — executing JS so dynamic content is visible to crawlers
- Noindex — directive telling search engines not to index a page
- Prioritization — ranking issues by predicted impact so the most valuable fixes come first
Under the hood: ML, NLP, and automation triggers [#under-the-hood]
At the core of ai seo auditing is a learning loop. Machine learning models cluster patterns—duplicate titles, canonical conflicts, redirect chains—while NLP evaluates content relevance, headings, and semantic overlap. These models combine with change-tracking and automation triggers to run targeted checks when something shifts, not just on a timer.
Automation triggers are your quiet sentries. A template updated? The system re-crawls affected paths, runs JavaScript rendering if needed, and scores the change. If severity crosses a threshold, it fires alerts, attaches impact estimates, and suggests owners. This is how an automated site audit stops being a static report and becomes a responsive system.
Mini case—accidental noindex on a core template:
- Scope: Product template affecting 312 URLs in /product/.
- Detection cue: Anomaly detection flagged a sudden spike in noindex counts and a dip in index coverage for that cluster.
- Priority: Critical, given these pages drove ~28% of organic entrances.
- Fix: Remove the unintended noindex directive in the base template; confirm correct canonicals and sitemap lastmod.
- Validation: Staging-first crawl to confirm cleanup, then immediate production re-crawl to verify recovery.
Audit types your seo audit tool should cover [#audit-types-seo-audit-tool]
A modern seo audit tool should span four pillars so you can act with confidence:
- Technical SEO audit: status codes, redirect chains, robots directives, canonicalization, hreflang, index coverage, JavaScript rendering, Core Web Vitals, mixed content, crawl budget efficiency.
- On-page analysis (often covered by on-page seo tools): titles, meta descriptions, headings, internal linking, structured data validation, image alt coverage, entity extraction and alignment with search intent.
- Content quality: thin or near-duplicate clusters via semantic deduplication, cannibalization risks, topical depth, and content-to-intent fit.
- Link analysis: broken internal links, orphaned pages, internal PageRank distribution, and trends in referring domains where available. Breadth matters, but context matters more. The best systems join findings across pillars—e.g., combining index coverage drops with canonical conflicts—to elevate what truly moves the needle.
From data to decisions: insight surfacing [#data-to-decisions]
AI systems distill sprawling crawl data into clean, ranked recommendations. They deduplicate overlapping symptoms, attach confidence scores, and forecast impact by tying issues to affected templates, traffic share, and ranking potential. That sequencing spares you from whack-a-mole triage and points straight at the highest-value fixes.
Expect three outputs: a prioritized list, a rationale, and a route to resolution. The list orders issues by predicted impact; the rationale shows “why this matters” with trend deltas and affected URL counts; the route prescribes fix steps and validation checks. That’s how raw diagnostics become decisions, and decisions become outcomes.
Setting Up an Automated SEO Audit Workflow [#set-up-workflow]
Quick Start [#quick-start-automate-seo-audit]
- Choose an AI SEO audit tool with technical, on-page, content, and link analysis.
- Connect your site and sitemaps; configure crawl depth and rendering.
- Schedule recurring audits and set alert thresholds.
- Customize rules and priorities for your site.
- Integrate with your project management tool to auto-create tasks.
- Review findings, fix issues, and re-crawl to validate; iterate thresholds to reduce noise.
Select the right AI seo audit tool [#select-seo-audit-tool]
Choose capabilities, not logos. At minimum, look for machine learning clustering, NLP-driven content evaluation, anomaly detection, JavaScript rendering, and impact-based prioritization. The tool should orchestrate both scheduled crawls and event-driven checks triggered by site changes.
Evaluate integrations and scale. You want alerts to flow into team chat (e.g., Slack/Email) and the option to create tickets via webhooks or APIs in your tracker. Confirm crawl limits, concurrency, and environment segregation (staging vs. production). Finally, consider data controls and support: access roles, audit logs, export options, and responsive guidance when you hit thorny technical seo audit edge cases.
Connect your site and define crawl parameters [#connect-and-crawl]
Start by verifying the domain, submitting sitemaps, and confirming robots handling. If parts of the site sit behind authentication, configure credentials or an allowlisted user agent. Map the key sections and templates you care about first to accelerate early signal.
Set rendering and scope precisely. Enable JavaScript rendering where content depends on it; define crawl depth and rate limits to respect infrastructure; select device profiles (mobile and/or desktop) to mirror your audience. Tight parameters reduce noise and make your first automated site audit fast, focused, and frictionless.
Schedule, alerts, and rules [#schedule-alerts-rules]
Tune frequency to site velocity. High-change sections may warrant daily crawls with anomaly detection always on; stable sections may run weekly. Define alert thresholds by severity, confidence, and affected URL count so only meaningful patterns page your team.
Codify exceptions and regression guards. Add exception lists for known duplicates (e.g., pagination) and explicit rules for template-level directives (e.g., alert if any noindex appears on core templates). Map severities to SLAs so “Critical” routes to the right owners quickly and “Minor” lands in a backlog bundle.
Pro Tip: Use confidence + impact as your twin gates for alerts. Require both to exceed thresholds to reduce chatter while preserving coverage.
Integrations and governance [#integrations-governance]
Real-time alerts should reach the humans who can act. Most teams route high-severity notifications to chat tools like Slack or Email. To create issues in trackers (e.g., Jira), teams typically either use the official issue-tracker app inside their chat tool to convert alerts into tickets or configure a custom webhook/API automation that posts directly to the tracker—be mindful that a native, direct integration is not universally available.
Establish ownership and SLAs by category (Technical, Content, Links) and adopt staging-first validation for risky changes. Document your escalation ladder, rollback plan, and verification steps (targeted re-crawl, HTML diff, structured data check, Core Web Vitals snapshot). Good governance turns seo automation tools into a reliable production system, not an occasional report.
Interpreting Automated SEO Audit Findings [#interpret-findings]
Read your seo audit tool report like a pro [#read-seo-audit-tool-report]
Automated reports deliver depth at a glance—if you know where to look. Start with the severity badge, which signals how urgent an issue is for your technical seo audit, and pair it with the confidence score. Severity reflects potential impact; confidence reflects the model’s certainty. High-severity, high-confidence items demand action; low-confidence items invite validation before escalation.
Next, scan affected templates and URLs. Many issues emerge at the template level, so one fix can resolve hundreds of pages. Review the impact estimate, often expressed as “traffic at risk,” “rank exposure,” or “affected entrances.” Look for trend deltas—sparklines that show when an issue appeared or spiked—so you can separate regressions from longstanding cleanup.
Most ai-powered seo reports also include AI-generated recommendations and validation steps. These are your fast path to action. Treat them as a first draft of the fix plan: confirm the recommendation fits your environment, then add owners, dependencies, and a target ETA before you push it into your workflow.
Prioritize for impact [#prioritize-for-impact]
Prioritization converts findings into results. Use a transparent model that balances business stakes, SEO potential, effort, and risk. The goal is to rank issues across categories—technical, on-page seo tools findings, content—so the next sprint tackles what moves the needle most.
Inputs and default weights:
-
BusinessImpact (B), wB = 0.35
-
SEOImpact (S), wS = 0.35
-
Ease (E), wE = 0.20
-
Risk (R), wR = 0.10 Formula:
-
PriorityScore = 100 × [ (wB×B) + (wS×S) + (wE×E) − (wR×R) ] / 5 Severity bands:
-
Critical (≥ 80)
-
Major (60–79)
-
Moderate (40–59)
-
Minor (< 40) Example 1 — Accidental noindex on a core template:
-
Inputs: B=5 (revenue pages), S=5 (indexation at risk), E=4 (single template), R=1 (low side effect)
-
Weighted sum = (0.35×5) + (0.35×5) + (0.20×4) − (0.10×1) = 4.20
-
Score = 100 × (4.20 / 5) = 84 → Critical Example 2 — 3xx redirect chains in navigation:
-
Inputs: B=4 (sitewide nav), S=4 (crawl/link equity), E=3 (moderate cleanup), R=2 (limited risk)
-
Weighted sum = (0.35×4) + (0.35×4) + (0.20×3) − (0.10×2) = 3.20
-
Score = 100 × (3.20 / 5) = 64 → Major This scoring keeps you honest. It prevents cosmetic items from crowding out structural fixes and helps justify trade-offs to stakeholders. You can also tune weights for your context (e.g., content-led sites might boost SEOImpact slightly) while preserving the same decision logic.
Triage guide from your seo audit tool findings.
Full Issue Triage Table schema fields:
- IssueID
- Issue
- Category
- Severity
- PriorityScore
- Why It Matters
- Affected URLs
- Recommended Action
- Owner
- Dependencies
- ETA
- Status
- Validation Steps
- Notes/Exceptions
- Confidence
Avoid common misreads [#avoid-misreads]
AI is precise, but context still counts. Guard against four frequent misreads during interpretation and triage.
- False positives on JavaScript-rendered pages:
- Symptom: The automated site audit flags missing content or links that actually load client-side.
- What to do: Confirm the crawl profile used JS rendering; spot-check rendered HTML; validate with a targeted re-crawl of a few representative URLs.
- Decision: If rendering was disabled or timed out, re-run with proper rendering before escalating.
- Cosmetic issues misclassified as critical:
- Symptom: Title length warnings or decorative image alt suggestions marked as high severity.
- What to do: Check the impact estimate and traffic at risk; apply the PriorityScore model to downweight low business/SEO impact.
- Decision: Reclassify as Moderate or Minor and batch-fix later.
- Context-specific exceptions (pagination, facets, UTM variants):
- Symptom: Duplicate content or canonical conflicts across predictable patterns.
- What to do: Confirm that pagination rel/next/prev (or equivalent pattern handling) and canonicals are correctly applied; add exception rules for known, low-value parameters.
- Decision: Suppress noise with documented exception lists and revisit if impact rises.
- Over-attribution to a single cause:
- Symptom: Index coverage dips assumed to be canonicals only.
- What to do: Cross-check robots, sitemaps, status codes, and noindex directives; scan trend deltas for concurrent template changes.
- Decision: Validate each hypothesis in staging or with a limited-scope re-crawl before launching a broad fix. By validating severity against confidence, confirming rendering, and codifying exceptions, you keep your ai-powered seo insights actionable—not alarmist.
Integrating Automated Audits into Ongoing SEO Processes [#integrate-into-process]
Cadence and collaboration [#cadence-collaboration]
Operational excellence turns “great reports” into measurable gains. Set a cadence that mirrors your release rhythm and site volatility: high-change areas get daily or near-daily checks; stable archives may run weekly. Build a short, standing triage ritual where SEO, engineering, and content review Critical and Major items, confirm owners, and set SLAs.
For communication, let real-time alerts route to team chat (e.g., Slack/Email) so the right people see the signal immediately. Use concise summaries that include severity, confidence, affected templates, and a one-line recommendation. Then, convert qualified alerts into trackable work via your issue tracker so progress, dependencies, and validation never get lost in the stream.
From finding to fix: automation in action [#finding-to-fix]
Think of the process as a state machine—each transition is explicit, observable, and reversible if needed.
- Trigger:
- An audit run or anomaly (e.g., surge in 5xx or noindex) fires.
- Rule evaluation:
- Your rules assess thresholds, confidence, exceptions, and dedupe related findings into a single, normalized issue.
- Task creation:
- A ticket is created in your issue tracker using either the official issue-tracker app inside chat to convert the alert to an issue or a custom webhook/API automation; avoid assuming a native, direct integration exists.
- Ownership & SLA:
- Assign by category—Technical (Engineering), Content (Editorial), Links (Content/Outreach). SLAs map to severity: Critical first, Major next, Moderate and Minor batched.
- Fix:
- Implement in staging first when feasible; link the PR or content edit in the ticket.
- Pre-merge QA:
- Run a targeted re-crawl of affected URLs/templates; validate structured data, canonical directives, and Core Web Vitals snapshots; perform manual spot checks for edge cases.
- Post-deploy verification:
- Re-crawl after release; confirm the issue’s trend delta reverses and the Confidence improves toward resolution.
- Closeout & learning:
- Close the ticket, capture Notes/Exceptions, and adjust rules to reduce future noise.
- Escalation/rollback (if verification fails):
- Reopen the ticket, escalate severity or revert changes, and run a short post-mortem to harden guardrails. The result is a loop where each finding has a clear fate, and each fix has proof. This is how seo automation scales beyond one-off cleanups into a dependable delivery pipeline.
Continuous monitoring and alert hygiene [#continuous-monitoring]
Continuous seo monitoring works only if alerts are informative, not incessant. Start by tuning thresholds along two axes: confidence (how sure the system is) and impact (how much traffic or rank is at stake). Require both to exceed your bar before auto-creating work. For lower-confidence patterns, send a chat-only heads-up and wait for a corroborating signal (e.g., a second audit or analytics hint).
Deduplicate relentlessly. Cluster issues that share a root cause—one template change shouldn’t generate 50 separate tickets. Maintain exception lists for benign patterns like pagination and tracking parameters, and revisit them periodically to avoid masking real regressions. Finally, review alert volume vs. true positives each sprint; if noise creeps up, adjust severity mappings, tweak rules, or scope crawls to the most consequential sections.
Governance notes:
- Real-time alerts can route to team chat (e.g., Slack/Email) for rapid awareness.
- Ticket creation in issue trackers (e.g., Jira) typically uses either the official issue-tracker app inside chat to convert alerts to issues or a custom webhook/API automation; don’t assume a universal native, direct integration.
- Recommend ownership by category (Technical, Content, Links); attach SLAs by severity and enforce staging-first validation for risky changes. With disciplined hygiene—threshold tuning, deduplication, and exception controls—your automated pipeline stays sharp, steady, and trusted across teams.
Troubleshooting and Advanced Tips for AI SEO Audit Automation [#troubleshooting]
Even the smoothest ai seo setup will encounter edge cases. Troubleshooting is less about firefighting and more about formalizing guardrails so your pipeline stays reliable under real-world change. Use these patterns to resolve blockers quickly and elevate signal quality across your seo automation tools.
Common blockers, quick fixes [#common-blockers]
JavaScript rendering hiccups can mislead audits. If content or links appear “missing,” confirm your profile uses rendered HTML and check for timeouts on heavy components. Re-run a targeted crawl on representative URLs, then validate with a small rendered sample before escalating.
Coverage gaps often point to robots directives, authentication walls, or sitemap omissions. Verify robots rules, ensure credentials are configured for gated areas, and reconcile submitted sitemaps with discovered URLs. Watch for URL patterns that explode combinatorially (facets, parameters); narrow the crawl scope or add parameter handling to avoid noise and wasted budget.
Integration friction usually traces back to mismatched assumptions. Real-time alerts can route to team chat, while ticket creation in issue trackers typically happens via the official issue-tracker app inside chat or a custom webhook/API automation. Document the path from alert to ticket, and test with a harmless, known issue to validate the flow.
FAQ callout
- Why am I seeing false positives on JavaScript-rendered pages?
- Likely cause: non-rendered crawls or render timeouts. Verify the crawl profile uses JavaScript rendering, spot-check the rendered DOM, and run a targeted re-crawl. If timeouts persist, raise the render timeout or exclude heavy test pages from broad checks.
- The audit is missing pages—what’s wrong with my crawl?
- Check robots directives, authentication, and sitemaps. Confirm canonicalization isn’t excluding the pages, ensure rendering is on for JS-dependent content, and review URL patterns (facets, pagination) that may require explicit inclusion rules.
- How do I reduce alert noise without missing critical issues?
- Tune thresholds with two gates: confidence and impact. Deduplicate related findings, maintain exception lists for benign patterns (pagination, tracking parameters), and require multiple signals (e.g., anomaly + scheduled run) before auto-creating tickets.
Custom models and rules [#custom-models-rules]
Your site’s structure and business model deserve tailored logic. Start by customizing issue weighting: elevate BusinessImpact for revenue-driving templates and boost SEOImpact for evergreen, high-visibility content. Incorporate the tool’s confidence score; downweight low-confidence items so they prompt verification rather than immediate work.
Create exception lists for known duplicates, facets, and pagination patterns that are legitimate by design. Then add regression checks targeting fragile templates—noindex, canonical, hreflang, and internal link regressions should trip Critical when they appear in core layouts. Over time, codify “approved deviations” in rules so exceptions remain explicit, not accidental.
Pro Tips:
- Staging-first rules and regression checks: require high-severity template changes to pass staged crawls before merging.
- Exception lists for pagination/facets: whitelist parameter patterns that are intentionally de-duplicated or canonicalized.
- Custom weighting by business impact: tune confidence thresholds and PriorityScore to reflect revenue or conversion proxies.
- Webhook/API guardrails: auto-create tickets with templates that include recommended actions, owners, and validation steps.
Staying ahead [#staying-ahead]
AI models evolve, and so does your site. Establish a quarterly tuning loop: review alert precision, adjust thresholds, and re-balance weights to reflect current priorities. Track schema changes, indexation rules, and page experience signals so your checks stay aligned with how search engines evaluate quality and performance.
Pair this with release-aware monitoring. When a major template or navigation ships, trigger focused re-crawls on the affected cluster, compare before/after signals, and use your validation checklist (status codes, canonical integrity, schema validity, Core Web Vitals snapshots). This steady cadence keeps your automation modern, measured, and trustworthy.
Measuring Success: KPIs and Continuous Improvement [#measuring-success]
You don’t just automate audits; you automate improvement. Measurement turns your seo audit tool into an operating system where insights compound and processes sharpen over time.
KPIs that matter [#kpis-that-matter]
Focus on a tight set of metrics that reflect velocity, quality, coverage, and outcomes:
-
Audit frequency: runs per month by section; higher velocity for high-change areas.
-
Detection-to-triage time: minutes or hours from alert to owner acknowledgment.
-
MTTR by severity: mean time to resolution for Critical/Major/Moderate issues.
-
Issue aging: average days open by severity cohort.
-
Indexed coverage: indexed pages divided by submitted or known pages.
-
Core Web Vitals pass rate: share of relevant pages passing thresholds.
-
Alert precision: true positives divided by total alerts.
-
Validation pass rate: share of fixes that pass automated checks on first try. Formulas to keep handy:
-
MTTR = Sum of resolution times / Resolved issues (by severity)
-
Alert Precision = True positive alerts / Total alerts
-
CWV Pass Rate = Pages passing all measured CWV thresholds / Total measured pages
-
Indexed Coverage = Indexed / Submitted
Turning data into strategy [#data-into-strategy]
Use trends, not single points. If MTTR for Critical issues improves while issue aging for Moderate balloons, rebalance resources or batch lower-severity fixes into sprints. When alert precision climbs, you can safely widen coverage or lower thresholds; if it drops, tighten exception lists and dedupe rules.
Tie outcomes to roadmap decisions. Indexed coverage up but Core Web Vitals lagging? Prioritize performance work on top templates. Orphaned pages dropping but duplicates persisting? Double-down on canonical and internal linking cleanup. With seo automation in place, each sprint becomes a practice in prediction and proof.
Automation impact on SEO KPIs
| KPI | Baseline | Current | Change | Insight/Next Step |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audit frequency (runs/month) | 1 | 30 | +29 | Daily for critical sections; weekly for stable areas. |
| Detection-to-triage time | 5 days | 1 hour | −4d 23h | Keep thresholds tuned; maintain chat alerts for Critical. |
| MTTR (Critical) | 10 days | 2 days | −8 days | Enforce staging-first checks to sustain speed without risk. |
| MTTR (Major) | 20 days | 9 days | −11 days | Assign clear owners; reduce handoffs. |
| MTTR (Moderate) | 40 days | 20 days | −20 days | Batch into sprint-ready bundles. |
| Indexed coverage | 88% | 95% | +7 pp | Continue canonical cleanup; prune low-value URLs. |
| Core Web Vitals pass rate | 60% | 78% | +18 pp | Optimize images; fix CLS on key templates. |
| Duplicate content clusters | 46 | 12 | −34 | Keep consolidating; update internal links to the canonical. |
| Redirect chains (3xx) | 140 | 30 | −110 | Add regression tests for link targets. |
| Orphaned pages | 380 | 120 | −260 | Integrate linking rules into publishing workflows. |
| Alert precision | 55% | 85% | +30 pp | Maintain exception lists; refine confidence thresholds. |
| Validation pass rate | 70% | 92% | +22 pp | Standardize validation steps in tickets. |
| Organic sessions (index) | 100 | 112 | +12% | Attribute gains by cluster; invest in top performers. |
These KPIs close the loop: your seo audit tool detects, your team acts, and the dashboard demonstrates progress with clarity that earns stakeholder confidence.
Conclusion: Next Steps for Modern SEO Teams [#conclusion]
Recap and action plan [#recap-action-plan]
You’ve seen the arc: why automation matters, how AI interprets your site, how to set up the workflow, how to read results, and how to integrate and measure. The play is simple:
- Start small: automate one audit path on a high-impact template.
- Tune thresholds: use confidence and impact gates to cut noise.
- Prove the loop: fix, re-crawl, validate, and show KPI movement.
- Scale: expand coverage section by section, then roll out org-wide. This approach blends ai seo strengths with human judgment, turning bursts of effort into a steady drumbeat of improvement.
Where to go next on this page [#where-to-go-next]
- Skip to Setup → #set-up-workflow
- See Troubleshooting → #troubleshooting
- Track Impact with KPIs → #measuring-success With disciplined governance, targeted rules, and continuous measurement, seo automation becomes more than monitoring—it becomes mastery.
{
"@context": "<https://schema.org>",
"@type": "HowTo",
"name": "Automate an SEO Audit with an AI-Powered SEO Audit Tool",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai>"
},
"description": "Step-by-step instructions to select, configure, and run an automated site audit using AI, then integrate findings into your workflow for continuous optimization.",
"inLanguage": "en",
"totalTime": "PT90M",
"image": [
"<https://example.com/images/manual-vs-ai-seo-audit-infographic.png>",
"<https://example.com/images/ai-seo-audit-dashboard-annotated.png>",
"<https://example.com/images/automated-seo-audit-workflow-diagram.png>",
"<https://example.com/images/ai-seo-audit-setup-checklist.png>"
],
"supply": [],
"tool": [
{
"@type": "HowToTool",
"name": "AI-powered SEO audit tool"
},
{
"@type": "HowToTool",
"name": "Project management or issue tracking software"
},
{
"@type": "HowToTool",
"name": "CMS or code repository access"
}
],
"step": [
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Choose an AI SEO audit tool",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-1>",
"text": "Select a seo audit tool with technical, on-page, content, and link analysis features, plus integrations for alerts and task creation.",
"image": "<https://example.com/images/ai-seo-audit-dashboard-annotated.png>"
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Connect and verify your site",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-2>",
"text": "Verify ownership, add sitemaps, and configure robots/auth handling to ensure complete crawl coverage."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Configure crawl parameters",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-3>",
"text": "Set crawl depth, rate limits, JavaScript rendering, and mobile/desktop user agents to match your environment."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Schedule recurring audits",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-4>",
"text": "Run daily or weekly scans depending on site size and change velocity for continuous monitoring.",
"image": "<https://example.com/images/automated-seo-audit-workflow-diagram.png>"
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Define rules and alerts",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-5>",
"text": "Set thresholds for severity, confidence, and affected pages. Create exception lists for known patterns (e.g., pagination)."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Integrate task creation",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-6>",
"text": "Connect alerts to your PM tool via native integrations or webhooks so issues auto-create tickets with owners and SLAs."
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Review, fix, and validate",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-7>",
"text": "Prioritize issues by impact and effort. Implement fixes, then re-crawl and validate with automated checks and spot testing.",
"image": "<https://example.com/images/ai-audit-report-annotated.png>"
},
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"name": "Iterate thresholds and coverage",
"url": "<https://example.com/blog/automating-seo-audits-ai#step-8>",
"text": "Reduce noise, refine rules, and expand coverage to sustain signal quality and performance gains.",
"image": "<https://example.com/images/ai-seo-audit-setup-checklist.png>"
}
],
"keywords": [
"seo audit tool",
"seo automation",
"ai seo",
"automated site audit",
"technical seo audit"
]
}