The Ultimate Guide to Building AI SEO Automation Workflows from Scratch
Manual SEO can feel like moving mountains with a teaspoon—repetitive, rote, and ruinous to momentum. AI SEO automation flips the script: it connects your data, models decisions, and moves work forward with measurable, repeatable precision. In short, AI SEO Automation Workflows transform one-off tasks into an operating system for growth.
Posted by
Related reading
The Ultimate Guide to AI Powered SEO Content Strategy
Picture this. It’s Monday, 8:30 a.m., coffee in hand. You’re juggling 1,200 keywords in a spreadsheet, opening 11 tabs to compare SERPs, building briefs by hand, and begging teammates for internal link suggestions. By noon, you’ve written… a title. Now flip it. You upload those queries into an AI-orchestrated workflow. It clusters them by search intent, drafts a brief with entities to cover, surfaces internal link opportunities, and flags gaps against competitors. By noon, you’re editing a strong draft and planning the next cluster.
How to Choose the Best AI SEO Tools for Your Content Workflow
Atlas Content had the right people. Smart strategists, solid writers, a reliable dev. But their SEO workflow was stuck in the past. They were juggling keyword research in spreadsheets, copying SERP data into briefs, and manually grading content against competitors. Technical checks lived in a separate crawler export. Monthly reporting took three days and stole time from strategy. Sound familiar?
Streamlining Your SEO Workflow with All-in-One AI Tools
You know the drill. Five tabs open for keyword research, a spreadsheet for mapping topics, a separate crawler, a content editor plugin, and a reporting deck that takes half a day to update. By Friday, you’ve spent more time stitching tools together than actually moving rankings.
The Ultimate Guide to Building AI SEO Automation Workflows from Scratch
Understanding AI SEO Automation: Foundations and Benefits
Manual SEO can feel like moving mountains with a teaspoon—repetitive, rote, and ruinous to momentum. AI SEO automation flips the script: it connects your data, models decisions, and moves work forward with measurable, repeatable precision. In short, AI SEO Automation Workflows transform one-off tasks into an operating system for growth.
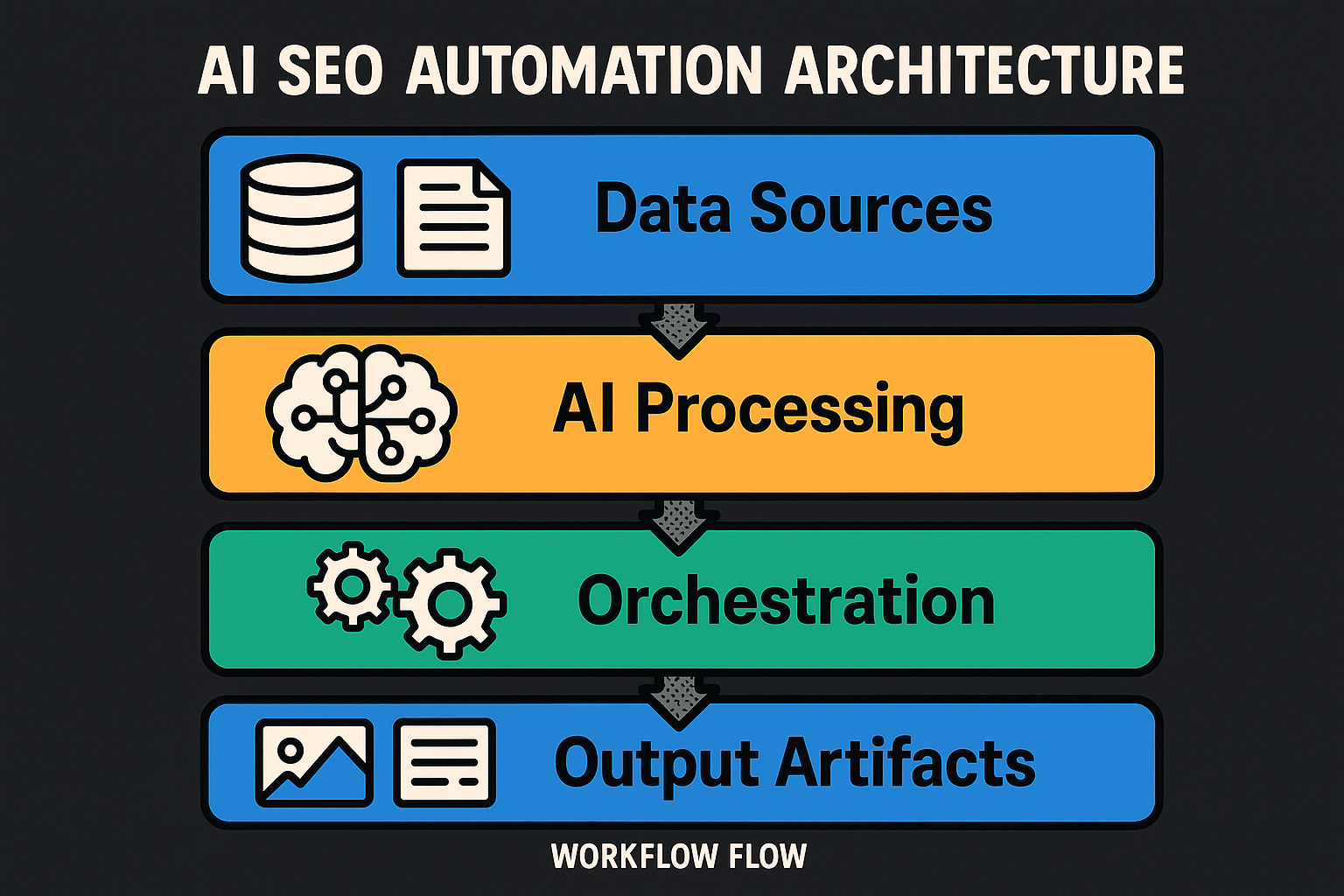
What it is AI-powered SEO automation uses machine learning models, APIs, and rule-based triggers to discover opportunities, analyze competitors, and optimize content at scale. The nervous system is simple and strong:
-
Data sources: Google Search Console (queries, clicks), analytics (engagement, conversions), SERP data via reputable APIs (e.g., SerpAPI, DataForSEO), crawler exports, and your CMS content inventory.
-
AI/ML layer: large language models (LLMs), embeddings for semantic clustering, classifiers for intent and link risk, and anomaly detection for technical health.
-
Orchestration: iPaaS and workflow engines, schedulers, and webhooks to move data and trigger actions.
-
Outputs: content briefs, on-page recommendations, internal link targets, prioritized audit tickets, dashboards, and alerts. Why it matters
-
Efficiency: AI accelerates repetitive work like keyword clustering, intent analysis, and content optimization, dramatically reducing manual hours (AIMultiple; ResultFirst; SuperAGI). Sources: AIMultiple, ResultFirst, SuperAGI
-
Scalability: Orchestrated pipelines expand from one site or market to many without proportional headcount.
-
Accuracy: AI augments judgment with semantic and intent-aware analysis for better query-to-content fit (AIMultiple; ResearchFDI; SuperAGI). Sources: AIMultiple, ResearchFDI, SuperAGI
-
Faster learning cycles: Continuous SERP monitoring via APIs (SerpAPI, DataForSEO) surfaces shifts fast, so you can adapt content and linking before competitors. Sources: SerpAPI, DataForSEO, WhitworthSEO A quick before-and-after An anonymized B2B SaaS content team previously spent about 22 hours per two-week cycle on manual keyword expansion, spreadsheet-based clustering, brief creation, and ad-hoc on-page checks. After deploying a modest automation stack—GSC exports + SERP snapshots (SerpAPI/DataForSEO) into embeddings-based clustering and intent classification, LLM brief generation, and automated crawler alerts—effort dropped to roughly 7 hours per cycle (≈68% time saved). Content velocity rose from 12 to 18 articles per month as strategists pivoted from busywork to judgment calls. This pattern echoes industry findings: AI streamlines repetitive tasks while improving content-to-query alignment and outcomes (AIMultiple; ResultFirst; SuperAGI).
The upshot: seo automation isn’t about replacing strategy; it’s about removing friction so strategy can lead.
Mapping Your SEO Automation Workflow: Key Processes to Automate
Think of your program as a pipeline: inputs in, insights out, improvements shipped. The following processes are prime candidates for ai seo acceleration and control.
- Keyword discovery, clustering, and intent classification
- Automate discovery from GSC, SERP APIs, and competitor URLs.
- Use embeddings and clustering to group semantically similar queries; classify intent (informational, commercial, transactional) with lightweight classifiers.
- Trigger brief creation when a new cluster crosses a volume or opportunity threshold.
- Content optimization with on-page seo tools
- Generate AI-assisted briefs with recommended H1–H3, entities, FAQs, and internal link targets derived from top SERP content and knowledge graphs.
- Suggest on-page enhancements: meta tags, schema hints, image alt text, and entity coverage.
- Always route changes through a human review gate before publishing.
- Competitor tracking with automated SERP diffs
- Schedule daily SERP snapshots for priority clusters using SerpAPI or DataForSEO.
- Compute diffs to detect rank swings, featured snippet gains/losses, and new entrants.
- Alert the team and create tickets for counter-moves (e.g., refresh a brief, expand a section).
- Backlink analysis and risk assessment
- Use classifiers to flag toxic or risky links and to prioritize outreach prospects.
- Combine link index data with analytics (conversions, assisted value) to score impact.
- Output prospect lists and risk reports; keep disavow decisions human-in-the-loop.
- Routine technical audits and crawler-driven alerts
-
Run scheduled crawls; apply rules and anomaly detection to surface broken links, duplicate content, canonical/hreflang misconfigurations, or Core Web Vitals regressions.
-
Auto-prioritize issues by severity and estimated impact; open tickets with reproduction steps. Process map narrative (how data flows)
-
Trigger: New SERP data arrives daily; crawl completes weekly; a post is published in CMS.
-
Data lane: GSC, analytics, SERP APIs, and crawler outputs flow into a warehouse or data hub.
-
AI lane: Models cluster queries, classify intent, extract entities, and score issues.
-
Automation lane: If a cluster exceeds thresholds, generate a brief and route it to an editor; if a technical score drops, file a ticket and ping Slack; if a competitor captures a snippet, schedule a refresh.
-
Human lane: Strategists approve briefs and link maps; editors publish to staging; approvers promote to production. The loop closes with post-publish monitoring and alerts.
SEO Task → Automation Potential
| SEO Task | Manual Time (est.) | Automation Potential (Low/Medium/High) | AI Methods | Data Inputs | Output Artifacts | Human Review Required | Notes/Guardrails |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword discovery & clustering | 6–10 hrs | High | Embeddings, clustering, intent classification | GSC exports, SERP snapshots, competitor URLs | Cluster sheets with volumes and intent | Yes | Lock seed topics; cap cluster size; log decisions |
| Content briefs | 2–3 hrs/post | High | LLM, entity extraction, SERP diffing | Top SERP pages, brand guidelines, style guide | Brief docs (H1–H3, entities, FAQs) | Yes | Enforce brand and compliance rules; require approval |
| On-page optimization | 1–2 hrs/page | High | LLM, NLP scoring | Existing content, SERP features, schema | Meta, headings, entity gaps, internal link recs | Yes | Stage changes; diff review; limit automated edits/day |
| Competitor tracking (SERP diffs) | 2–4 hrs/week | Medium–High | SERP diffing, change detection | SerpAPI/DataForSEO daily snapshots | Movement reports, share-of-voice trends | Optional | Respect API rate limits; set alert thresholds |
| Backlink analysis & risk | 3–6 hrs/month | Medium | Classification, anomaly detection | Link index, analytics, CRM | Risk reports, PR prospect lists | Yes | Cautious disavow; document criteria and thresholds |
| Technical audits | 4–8 hrs/sprint | High | Rules engine, anomaly detection | Crawler exports, CWV, logs, GSC | Prioritized issue tickets, health score | Yes | Severity scoring, rollback plan, staging-first QA |
Citations and context
- Automated keyword clustering and intent analysis shorten research cycles while improving target alignment (AIMultiple; SuperAGI). Sources: AIMultiple, SuperAGI
- Entity-driven briefs and on-page recs strengthen semantic coverage and topical authority (AIMultiple; PageOptimizer insights). Sources: AIMultiple, PageOptimizer Pro
- SERP monitoring via SerpAPI or DataForSEO enables timely competitor diffs, with best practices around rate limits, scheduling, and compliance (SerpAPI; DataForSEO; WhitworthSEO). Sources: SerpAPI, DataForSEO, WhitworthSEO
- Continuous audits and Core Web Vitals checks preserve crawlability and user experience, foundational to sustained visibility (Google Search Central; web.dev). Sources: Google Search Central, web.dev As you connect these pieces, remember the principle that powers effective AI seo: automate the repeatable, elevate the reviewable, and concentrate human judgment where it compounds results.
Choosing the Right AI SEO Automation Tools and Platforms
Your stack should serve your strategy, not the other way around. The right seo automation software balances data quality, robust AI capabilities, and operational guardrails—then plugs neatly into your CMS, analytics, and orchestration layers.
Selection criteria that matter
- Data coverage and quality
- How broad and deep is the data (SERP features, historical depth, localized precision)?
- Does the provider document methodology and known limitations?
- Model capabilities
- LLM support for brief generation and on-page recs
- Embeddings for clustering and semantic similarity
- Classifiers for intent, link risk, and anomaly detection
- Integrability
- Mature APIs, webhooks, and SDKs
- Connectors for GSC/GA4, CMSs, iPaaS/orchestration, data warehouses (BigQuery/Snowflake), BI tools
- Governance and explainability
- Prompt and rule version control, audit logs of automated actions
- Human-in-the-loop gates before live changes
- Cost model fit
- Seat vs. usage vs. hybrid; forecastability under expected query/crawl volumes
- Security and privacy
- PII handling policies; encryption at rest and in transit; key rotation; least-privilege roles for service accounts
- Compliance and ToS
- Respect search engine terms; use reputable SERP providers with proxy management and ethical collection patterns
- Support and roadmap
- SLA, documentation, solution engineering, and an evolving roadmap aligned to your workflows For SERP monitoring and competitor tracking, reputable APIs such as SerpAPI and DataForSEO provide real-time or high-granularity snapshots, geo/device targeting, and SERP feature extraction—standard building blocks for automated rank tracking and diffs. Respect rate limits and implement retry/backoff strategies to avoid disruptions and maintain compliance SerpAPI, DataForSEO, WhitworthSEO, CodeClever, RapidSeedbox.
Integration considerations (patterns that scale)
- Connect core sources
- GSC and GA4 via native connectors or APIs into your warehouse; keep schema consistent for cluster mapping and CTR/position curves.
- SERP APIs (SerpAPI/DataForSEO) scheduled via cloud functions or iPaaS for daily snapshots; store raw and processed results (features, diffs) in BigQuery/Snowflake.
- Crawlers as your seo audit tool: export issue data and CWV insights to the warehouse for scoring and prioritization.
- CMS integration for content status and “content velocity” tracking; webhooks on publish/update to trigger audits and post-publish monitoring.
- Orchestration and ops
- Use iPaaS (Zapier/Make/n8n) or workflow engines (Airflow/Prefect/serverless queues) for triggers, fan-out processing, and backoff retries.
- Implement idempotency keys and message queues to avoid duplicate actions (e.g., repeated ticket creation).
- Downstream outputs
- Ticketing (Jira/Asana) for prioritized issues; chat alerts (Slack/Teams) for thresholds; BI dashboards (Looker/Data Studio/Tableau) for KPIs.
- Reliability and guardrails
- Rate-limit handling, exponential backoff on 429/5xx, and dead-letter queues for failed jobs.
- Secrets management (KMS/Vault), key rotation schedules, least-privilege service roles.
- Audit logs for all automated edits and prompt versions; staging-first release paths.
Vendor-neutral overview by function
- Keyword/SERP monitoring: Use SERP APIs for rank tracking, SERP feature extraction, and localized testing; favor speed (real-time reactions) or granularity (pixel rank, screenshots) based on your needs SerpAPI, DataForSEO.
- On-page seo tools: Content optimization platforms that propose entities, headings, FAQ gaps, and internal links; require human review before production.
- SEO audit tool and crawling: Deep crawls, JS rendering, and CWV insights with rules-based scoring and anomaly detection.
- Backlink intelligence: Link discovery, risk/toxicity scoring, and prospect lists connected to CRM/outreach.
- Orchestration and pipelines: iPaaS and workflow managers to stitch data, models, and actions into dependable AI SEO Automation Workflows.
AI SEO automation tools comparison
| Function | Key AI Features | Integrations | Pricing Model | Strengths | Best For | Notable Considerations (privacy/explainability) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword & SERP Monitoring (e.g., SERP APIs) | SERP feature extraction, geo/device targeting, rank diffs | Data warehouse, BI, Slack/Teams, schedulers | Usage-based | Speed, localization, scale | Real-time monitoring, competitor tracking | ToS compliance; proxy ethics; log query parameters without PII |
| On-Page SEO Tools | Entity/heading suggestions, brief generation, internal link mapping | CMS, GDocs, Git, Slack/Teams | Seat + usage | Editor workflow fit, semantic coverage | Content teams and editors | Require human-in-the-loop; version prompts and rules |
| SEO Audit Tool (Crawler) | Issue classification, JS rendering, CWV anomaly detection | GSC, GA4, Jira/Asana, BI | Seat or hybrid | Depth of crawl, technical precision | Tech SEO and platform teams | Respect crawl budgets; store PII-free logs; explain scoring |
| Backlink Intelligence | Link toxicity classifiers, prospect scoring, anchor text analysis | CRM/outreach, analytics | Seat or usage | Link depth, risk insights | PR/outreach and authority building | Disavow decisions remain human; document thresholds |
| Orchestration/iPaaS | Triggers, webhooks, retries/backoff, branching | APIs, DBs, Slack/Teams, ticketing | Tiered or usage | Integration speed, reliability | Ops and scale-out automation | Secrets management, audit trails, rollback paths |
| Data Warehouse/BI | Feature engineering, KPI modeling, dashboards | ETL/ELT, CMS, GSC/GA4, SERP APIs | Storage + seat | Single source of truth, analysis depth | Analytics and leadership | Access control (least privilege); encryption; data lineage |
What a consolidated dashboard should show
A practical AI SEO dashboard unifies:
-
SERP snapshots for tracked clusters (visibility and share-of-voice)
-
GSC clicks/impressions/position with CTR vs. expected curves
-
Crawler health and a technical score
-
Core Web Vitals pass rate
-
Content velocity (new/updated pages)
-
Alerts feed with thresholds Common alert thresholds and triggers:
-
Rank drop of ≥3 positions for a high-value cluster
-
Featured snippet lost for a target query
-
Technical Health Score How do I build an AI SEO automation workflow?
Define SEO objectives and KPIs. Map your processes (keyword research, content optimization, audits). Choose AI-powered tools with strong integrations. Connect data sources and set triggers (e.g., new keywords or crawl issues). Automate steps like clustering, brief creation, and audits with review gates. Test in staging, monitor KPIs, and iterate prompts and rules. Scale to more sites and teams once stable.
Step 1: Define objectives and KPIs
Anchor your workflow to measurable outcomes before writing a single line of integration code.
- What to set
- Objectives: increase qualified non-brand traffic, improve visibility for target clusters, reduce time-to-publish for optimized pages, harden technical health.
- KPIs (choose a leading and a lagging pair)
- Non-brand organic sessions (GA4)
- Share of Voice across tracked clusters (SERP snapshots)
- Content velocity (new or materially updated pages/week from CMS)
- Technical Health Score (crawler + Core Web Vitals)
- CTR vs. expected by position (GSC + CTR curve)
- Example KPIs to track now
- Share of Voice for 50 priority clusters
- ΔCTR (actual minus expected) on pages with updated titles/meta
- Technical Health Score by template type (e.g., blog, category, product)
- Triggers to define
- Weekly KPI snapshot trigger (time-based, every Monday 8:00 AM) that posts a digest to Slack and pins baselines.
- Tangible deliverable
- KPI specification document: definitions, formulas, data sources, owners, and alert thresholds. Include a one-page “North Star” metrics sheet for leadership.
Step 2: Map workflow stages, data flows, and triggers
Design the assembly line. Draw swimlanes to separate Data, AI, Automation, and Human Review; make trigger conditions explicit.
- Core data sources
- GSC for queries, clicks, positions; GA4 for sessions/conversions
- SERP APIs for daily snapshots and features
- Crawler exports (your seo audit tool) for issues and CWV
- CMS webhooks for publish/update events
- Stages and flows (example)
- Ingest: nightly GSC/GA4 exports; daily SERP snapshots; weekly crawls
- Transform: embeddings-based clustering; intent classification; entity extraction; issue scoring
- Decide: rule engine checks thresholds (e.g., cluster volume/opportunity, health score changes)
- Act: generate brief; open ticket; propose on-page changes; schedule monitoring
- Review: strategist/editor approval; technical sign-off
- Triggers to wire
- Time-based: daily SERP snapshot at 6:00 AM; weekly crawl Sunday 11:00 PM
- Event-based: CMS publish/update event; “new cluster > threshold” event; “Technical Health Score threshold” → generate brief → route to editor with due date
- “CMS publish” → run preflight on-page checks via on-page seo tools → stage → request approval
- “Crawl complete” → recompute Technical Health Score → open prioritized tickets for criticals
- Example KPIs for integration health
- Job success rate (% runs without error)
- Average end-to-end latency (ingest → action)
- Duplicate action rate (should be ~0 with idempotency)
- Triggers to confirm
- Webhooks from CMS; scheduled SERP jobs; crawl-complete events
- Tangible deliverable
- Integration config pack: API key inventory, scopes, endpoint catalog, field mappings, rate-limit policies, retry/timeout parameters, and a routing matrix (event → action).
Step 4: Test, launch in staging, and iterate
Treat automation like product. Prove quality in staging, then deploy with guardrails and version control for prompts and rules.
- Test plan
- Unit tests for parsers and mappers; sandbox runs for SERP and crawler pulls; golden datasets to verify clustering and intent outputs.
- Acceptance criteria
- ≥95% job success rate for seven consecutive days in staging
- Brief acceptance rate ≥80% without major edits
- Audit false-positive rate ≤10% on critical issues
- Guardrails and governance
- Human-in-the-loop gates for any live content or metadata change
- Prompt and rule versioning in source control; change logs with approver names
- Rollback procedures: disable automations with a single switch; revert changes via versioned drafts
- Example KPIs for stabilization
- Brief quality score (editor rubric)
- % of automated tickets accepted without reclassification
- Triggers to verify
- “Publish-to-staging” automatically runs on-page checks and schema validation before approval
- Tangible deliverable
- Test plan and runbook: failure modes, escalation paths, rollback steps, and a “kill switch” procedure.
Implementation checklist
- Objectives and KPIs defined with baselines
- Process diagram (swimlanes, triggers, gates) complete
- API keys secured; service accounts and permissions set
- Data mapping finalized; idempotency keys defined
- Automations configured in orchestration layer with retries/backoff
- Review gates and approver roles documented
- Test plan executed; acceptance criteria met in staging
- Dashboards and alerts live with thresholds
- Runbook published; rollback and kill switch verified
- Launch sign-off captured; iteration cadence scheduled
Troubleshooting and common issues
- API authentication failures
- Fix: rotate keys; confirm scopes/permissions; store in a secrets manager; test token refresh flows; add health checks for expired credentials.
- Rate limiting and transient errors (429/5xx)
- Fix: exponential backoff with jitter; respect provider quotas; batch requests; queue tasks; implement circuit breakers and dead-letter queues.
- Schema mismatches and nulls
- Fix: schema validation at ingestion; versioned schemas; fallback defaults; quarantine invalid rows; add “last schema change” notes to the runbook.
- Hallucinated or low-quality brief outputs
- Fix: constrain prompts; provide retrieval-augmented SERP/context; enforce length/entity thresholds; require human approval; maintain prompt versions and quality rubrics.
- Noisy internal link suggestions
- Fix: raise similarity thresholds; require entity overlap; cap suggestions per page; add “irrelevance” feedback loop to retrain rules.
- Staging vs. production confusion
- Fix: separate credentials and indices; prefix resources by env; color-code dashboards; disallow production writes from staging service accounts; enable an environment banner in CMS.
- Alert fatigue
- Fix: tune thresholds; add cooldown periods; bundle low-severity alerts into daily digests; route criticals to real-time channels only; require owner assignment on alert creation.
Monitoring and continuous review
- Set practical alert thresholds
- Technical Health Score < 90 → open ticket and page owner
- Rank drop ≥3 positions for a tracked cluster → alert and brief refresh suggestion
- ΔCTR below −3 percentage points for high-impression queries → title/meta test recommendation
- Content velocity < target by 20% → ops check on bottlenecks
- Establish cadences
- Daily: scan alerts; triage criticals
- Weekly: 30-minute ops review (SOV, ΔCTR, health score, issue backlog); update prompts/rules where error patterns persist
- Monthly: workflow retro and threshold recalibration; expand scope to new clusters or markets once stability holds Build once, then keep it breathing. With clear KPIs, explicit triggers, reliable integrations, and disciplined review gates, seo automation becomes a steady, scalable engine rather than a fragile collection of scripts. Your workflow will improve as your feedback does—ship, measure, refine, repeat.
Optimizing and Scaling Your AI SEO Automation System
Optimization turns a working pipeline into a winning program. Scaling makes it repeatable across teams, sites, and markets—without sacrificing governance or quality.
The KPI dashboard that powers iteration
Monitor leading indicators for fast course-correction and lagging outcomes for ROI. Pair each metric with a threshold and an action.
-
Organic Sessions (Non-brand)
-
Definition: Sessions from Organic Search excluding brand terms
-
Source: GA4 filtering or regex-based exclusion (GA4 supports custom segments and conversions)
-
Threshold: Alert if week-over-week drops by 15%+
-
Action: Investigate SOV, CTR delta, and recent technical regressions Source: GA4 Help Center
-
Share of Voice (tracked clusters)
-
Definition: Weighted visibility across tracked terms from SERP snapshots
-
Source: SERP APIs + rank tracker
-
Threshold: Alert if SOV falls by 10% week-over-week for a priority cluster group
-
Action: Refresh briefs; inspect snippet losses and competitor moves Context: Recent industry studies highlight SERP shifts and changing click dynamics, underscoring the need for visibility monitoring (Ahrefs; Semrush). Sources: Ahrefs, Semrush
-
CTR vs. Expected (ΔCTR)
-
Definition: Actual CTR minus position-based expected CTR
-
Source: Google Search Console (CTR, position)
-
Threshold: Alert per page when ΔCTR < −3 percentage points for high-impression queries
-
Action: Test titles/meta; enrich entities; improve FAQ coverage Source: GSC Help
-
Technical Health Score
-
Definition: Weighted issue scoring normalized to 0–100 (crawler + CWV)
-
Source: Your SEO audit tool + Core Web Vitals telemetry
-
Threshold: Alert if < 90 or drops by ≥5 points in a week
-
Action: Open tickets for critical issues; prioritize by impact Source: web.dev Core Web Vitals
-
Core Web Vitals Pass Rate
-
Definition: Percent of URLs passing LCP, CLS, INP thresholds
-
Threshold: Alert if pass rate declines by 10% for any template cohort
-
Action: Template-level fixes; rollbacks for regressions Source: web.dev Core Web Vitals
-
Content Velocity
-
Definition: Count of new or materially updated pages in a period
-
Source: CMS + orchestration logs
-
Threshold: Alert if weekly output misses target by 20%+
-
Action: Unblock briefs; adjust SLAs; expand contributors
-
Incremental Organic Revenue (modeled)
-
Definition: Modeled uplift vs. baseline controlling for seasonality and cannibalization
-
Source: GA4 + BI model
-
Threshold: Alert if negative for two consecutive months
-
Action: Re-evaluate cluster priorities, conversion paths, and internal linking Cadence for disciplined reviews
-
Daily (10–15 minutes): Triage alerts for critical rank drops, CWV regressions, or technical score dips; assign owners immediately.
-
Weekly (30 minutes): Review SOV trends, ΔCTR outliers, content velocity, and ticket backlog. Decide on prompt/rule updates and threshold tuning.
-
Monthly (60–90 minutes): Evaluate ROI and stabilization metrics, recalibrate thresholds, and approve scale-out to new clusters, sites, or markets.
Feedback loops for continuous improvement
Optimize your ai seo stack like a product—tight loops, small changes, clear evidence.
- Prompt iteration loop
- Collect editor scores on brief usefulness and accuracy.
- Add top-rated outputs to a “few-shot” library; prune poor examples.
- Constrain prompts with structured context (retrieval of SERP summaries, entities, guidelines) and explicit acceptance criteria.
- Version prompts; compare acceptance rate and edit distance before/after changes.
- Rule and threshold refinement
- Inspect false positives/negatives for audits and link recommendations.
- Adjust similarity thresholds, entity overlap requirements, and severity weights.
- Bundle low-severity alerts into digests to reduce noise; reserve real-time pings for criticals.
- Lightweight retraining approach
- Maintain a labeled “golden set” of cluster-to-brief pairs and link suggestions with pass/fail annotations.
- Retrain or re-weight small classifiers (intent/link-risk) monthly using the latest labels.
- For LLMs, prefer retrieval-augmented prompting plus curated few-shot examples; fine-tuning only when persistent gaps remain and data is robust.
- Track model drift: if acceptance metrics deteriorate for two periods, trigger a targeted retrain or prompt overhaul.
Governance for scaling across teams, sites, and markets
Scaling seo automation requires explicit permissions, documentation, and human-in-the-loop checkpoints.
- Roles and permissions
- Reader: view dashboards and logs
- Operator: run workflows, triage alerts, create tickets
- Editor/Strategist: approve briefs and on-page changes
- Admin: change prompts/rules/thresholds, manage API keys, approve releases
- Enforce least privilege; separate staging/production credentials
- Documentation
- For every workflow, document inputs, transformations, outputs, approvers, and rollbacks.
- Use version control for prompts, rules, and thresholds; tag releases with change notes.
- Human-in-the-loop gates
- No automated edits to live content or metadata without approval.
- Require second-check for high-impact changes (title rewrites on top pages, internal link changes on money pages).
- Route high-risk items to senior reviewers.
- Auditability
- Log every automated decision with timestamp, inputs, prompt/rule versions, and approver ID.
- Preserve raw SERP snapshots and crawler exports; store diffs to support explainability.
- Environment strategy
- Staging-first for all automated edits; run preflight checks and schema validation.
- Clear rollback paths; maintain a “kill switch” per workflow.
Optimization in action: Scenario B (anonymized)
Context: An in-house content team manages a topic hub with 200+ articles. Automated internal link recommendations became noisy—irrelevant links and overlinking to hub pages.
Interventions
-
Introduced similarity and entity-overlap thresholds (links must exceed a similarity score and share target entities).
-
Tuned the LLM prompt:
-
Don’t insert links above the first H2.
-
Cap at three new internal links per article.
-
Prefer contextual adjacency within the cluster.
-
Added a human review gate for tier-1 pages.
-
Measured outcomes via GSC (CTR/position) and GA4 (engagement), plus editor time-on-task logs. Results after six weeks
-
~40% fewer irrelevant link suggestions.
-
~12% median increase in time-on-page for hub pages.
-
~9% lower bounce rate for cluster pages.
-
50% less editor time vetting suggestions. Takeaway: Small, specific changes—prompt constraints, threshold tuning, and a review gate on critical pages—reduced noise and boosted both quality and efficiency.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices for AI SEO Automation
Pitfalls to avoid
-
Over-automation: shipping unreviewed content or meta changes directly to production.
-
Poor data hygiene: schema drift, nulls, and inconsistent tagging undermine AI decisions.
-
Black-box behavior: no logs, no diffs, no versioning—no trust.
-
Alert fatigue: thresholds too sensitive, no digesting, constant noise.
-
ToS and privacy risks: scraping without reputable providers; leaking PII into prompts or logs.
-
Staging shortcuts: pushing changes live without preflight checks or rollbacks. Best-practices checklist
-
Document every workflow: inputs, transformations, outputs, reviewers, and rollbacks.
-
Enforce human-in-the-loop for any change touching live content or metadata.
-
Validate data at ingestion: schema checks, null handling, outlier detection.
-
Version control prompts, rules, and thresholds; tag and annotate releases.
-
Use a staging environment first; require preflight checks and schema validation.
-
Log all automated actions and decisions; maintain audit trails with approver IDs.
-
Retrain/re-prompt on a regular cadence using labeled examples and acceptance metrics.
-
Implement alerting with sensible thresholds, cooldowns, and digest bundling.
-
Align governance with privacy and security policies; avoid PII in prompts and logs.
-
Run quarterly reviews of workflows and integrations; adjust thresholds to business seasonality. When in doubt, slow down to speed up. Prove changes in staging, keep your prompts and rules under version control, and let the data direct your next iteration. That’s how ai seo evolves from scripts to systems—and how AI SEO Automation Workflows scale without surprises.
Getting Started: Your Next Steps to AI SEO Automation Success
You’ve seen the full arc: define outcomes, map data and decisions, connect your tools, and govern the loop with dashboards and review gates. You can start small—one workflow, one market—then expand with confidence once signals stabilize. Done well, AI moves the repetitive out of the way so your strategy gets the spotlight. This is where AI SEO Automation Workflows turn scattered effort into a system that ships, learns, and scales.
Quick-start checklist
Use this concise plan to go from idea to first win:
- Clarify one primary objective (e.g., increase qualified non-brand traffic).
- Choose one workflow to automate first (for example: keyword clustering → brief creation).
- Inventory data sources (GSC, Analytics, SERP snapshots, crawler exports, CMS).
- Pick tools: keyword AI + on-page SEO tools + an SEO audit tool + orchestration platform.
- Map triggers and outputs (new keyword → cluster → brief doc → human review → publish).
- Set guardrails (token limits, max changes per day, required review gate, rollback plan).
- Pilot in staging; validate outputs with at least three sample pages.
- Define KPIs; set baselines and alert thresholds.
- Launch and iterate weekly; log changes, measure impact, and refine prompts/rules.