The Complete Guide to AI Search Optimization Strategie
You’ll learn how AI search engines and answer engines interpret intent, connect entities, and synthesize answers—and how to build content, structure, and workflows that win those answers while still earning clicks. Expect clear frameworks, real examples, and step-by-step tactics you can deploy now.
Posted by
Related reading
The Ultimate Guide to AI Powered SEO Content Strategy
Picture this. It’s Monday, 8:30 a.m., coffee in hand. You’re juggling 1,200 keywords in a spreadsheet, opening 11 tabs to compare SERPs, building briefs by hand, and begging teammates for internal link suggestions. By noon, you’ve written… a title. Now flip it. You upload those queries into an AI-orchestrated workflow. It clusters them by search intent, drafts a brief with entities to cover, surfaces internal link opportunities, and flags gaps against competitors. By noon, you’re editing a strong draft and planning the next cluster.
How to Choose the Best AI SEO Tools for Your Content Workflow
Atlas Content had the right people. Smart strategists, solid writers, a reliable dev. But their SEO workflow was stuck in the past. They were juggling keyword research in spreadsheets, copying SERP data into briefs, and manually grading content against competitors. Technical checks lived in a separate crawler export. Monthly reporting took three days and stole time from strategy. Sound familiar?
Streamlining Your SEO Workflow with All-in-One AI Tools
You know the drill. Five tabs open for keyword research, a spreadsheet for mapping topics, a separate crawler, a content editor plugin, and a reporting deck that takes half a day to update. By Friday, you’ve spent more time stitching tools together than actually moving rankings.
AI search is rewriting the rules of SEO. Are you ready to adapt?
This guide turns disruption into direction. You’ll learn how AI search engines and answer engines interpret intent, connect entities, and synthesize answers—and how to build content, structure, and workflows that win those answers while still earning clicks. Expect clear frameworks, real examples, and step-by-step tactics you can deploy now.
Quick answer: What are the best AI search optimization strategies?
- Lead with intent-first, task-oriented content that directly answers primary and follow-up questions.
- Structure pages for answer engines using concise summaries, scannable headings, lists, and step-by-step formats.
- Use structured data (Schema.org) to expose entities, relationships, and content types to AI systems.
- Optimize for conversational queries with natural language, definitions, examples, and disambiguation.
- Provide evidence: citations, expert commentary, original data, and transparent authorship.
- Engineer snippets: craft 40–60-word answer summaries and compelling meta/OG elements.
- Design for engagement signals: fast load, readability, clear hierarchy, and low bounce.
- Publish rich media (diagrams, tables, code blocks) that LLMs can quote and users value.
- Map entity ecosystems: align terms, synonyms, and related entities to a coherent topic graph.
- Monitor AI SERP features, zero-click behavior, and answer visibility; iterate from gaps.
- Support agentic AI: include how-tos, checklists, and action affordances that enable next steps.
- Build machine-readable trust with Organization, Person, Product, and Article schemas. Skip to Understanding AI Search
Understanding AI Search
The New Frontier
Traditional search matched strings. AI search matches meaning. That shift—from keywords to concepts, from isolated pages to interconnected entities—reshapes what “optimized” really means. Answer engines now synthesize multi-source responses, surface citations, and propose next actions. Agentic AI goes further, planning steps, invoking tools, and nudging users toward completion, not just comprehension.
Semantic search: a method that interprets the meaning behind queries by modeling entities (things, not strings), their attributes, and relationships. Entities: people, places, organizations, products, concepts—nodes in a knowledge graph that AI systems connect to interpret intent.
Traditional SEO focused on keywords and links; AI search optimization prioritizes intent, entities, structure, and engagement.
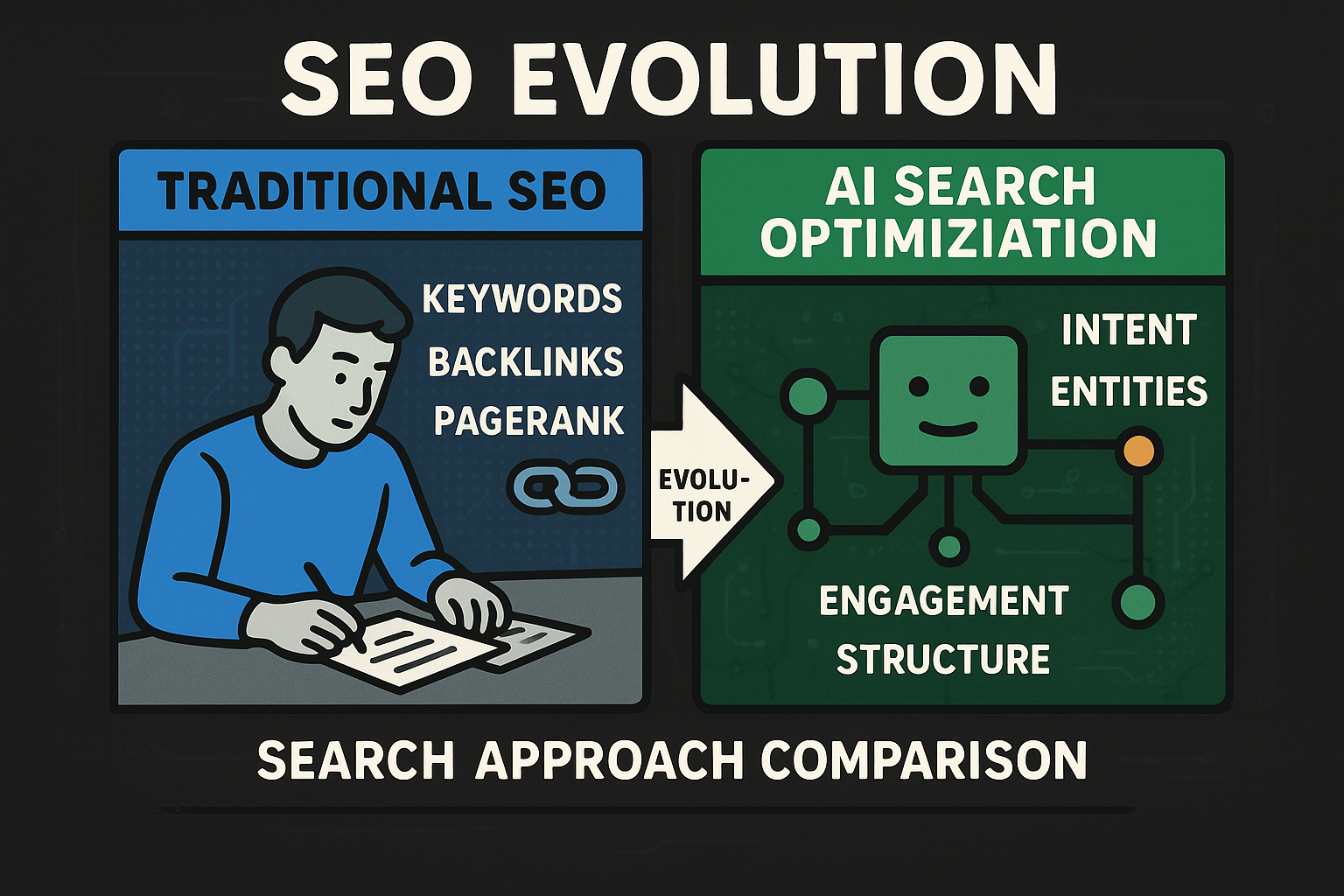
Comparison diagram showing the evolution from traditional SEO (keyword matching, backlinks, page rank) to AI search optimization (intent understanding, entity relationships, structured data, engagement signals)
From Queries to Conversations: How AI Interprets Meaning and Context
A query isn’t an isolated spark; it’s the first turn in a conversation. AI systems parse intent, detect entities, and infer sub-intents (define, compare, decide, do). They evaluate ambiguity and suggest clarifying follow-ups. Large language models (LLMs) then synthesize concise, citation-backed answers from multiple sources rather than lifting a single snippet.
- Intent resolution: systems classify the primary task and probable next questions.
- Entity linking: key concepts are mapped to a knowledge graph for context.
- Retrieval and reranking: diverse, authoritative sources are selected for coverage, clarity, and trust.
- Synthesis: LLMs compose the answer, resolve conflicts, and present the most actionable path forward. AI search transforms a query into intent, maps entities, retrieves diverse sources, and synthesizes a scannable answer.
Answer Engines and Zero-Click Outcomes: What They Prioritize
Answer engines aim to satisfy the task in the SERP. They reward pages that:
- Present direct, unambiguous answers in the first 40–60 words.
- Offer scannable support content—definitions, comparisons, steps, and pitfalls.
- Back claims with credible citations and clear authorship.
- Provide modular components (tables, diagrams, code examples) that are easy to quote.
- Reinforce meaning with schema markup, connecting your content to recognized entities. Expect more zero-click results. That doesn’t mean less opportunity; it means different opportunity. If your content is cited in an answer box or recommended as a follow-up, you earn trust and targeted clicks. The metric to watch shifts from “position” to “answer presence, citation prominence, and assisted action completion.”
Agentic AI in Search: From Retrieval to Task Completion
Agentic AI doesn’t just answer; it assists. It can:
-
Compare options (“X vs Y”), summarize trade-offs, and recommend a path.
-
Chain steps for complex tasks (plan → estimate → book → confirm).
-
Invoke tools and external data to verify claims or fetch specifics.
-
Offer next actions as links, checklists, or structured prompts. For marketers, this changes what “optimized” looks like. Your page should not only inform; it should equip. Include:
-
Clear, copyable checklists and step-by-step workflows.
-
Comparison matrices with criteria that matter to decision-makers.
-
Action affordances: calculators, templates, and links to APIs or demos.
-
Schema signals that make these components machine-readable. The outcome is a move from “ranking for keywords” to “being selected as reliable evidence for answers and as the next step for actions.”
The mindset shift you need
- From density to clarity: fewer redundant terms, more precise definitions.
- From monoliths to modules: break content into reusable, quotable components.
- From pages to graphs: connect your topics, entities, and schemas coherently.
- From visits to value: optimize for answer visibility, guided clicks, and completed tasks. In short, AI search optimization strategies anchor on intent, entities, and engagement. Build content that answers directly, prove it with structure and evidence, and package it so both users and AI systems can act on it. That’s how you earn visibility in answer engines and resilience as agentic AI becomes the norm.
Core Principles of AI Search Optimization
Answer engines reward pages that are succinct, scannable, and soundly sourced. The winning mindset blends three pillars: intent-first content that resolves tasks, semantic structure that maps meaning, and experience signals that prove users found value. These align with how AI Overviews and LLM-powered answer engines select sources—authority, semantic alignment, freshness, clean structure, and measurable engagement.
The pillars of AI search optimization: intent-first content, semantic structure, and measurable user engagement.
Callout — Why schema matters in AI answers: Schema clarifies “what this is” and “how parts relate,” improving eligibility for rich results and citations; validate with Google’s Rich Results Test and monitor enhancements via Search Console.
Intent-First, Task-First Content
Start with what the user wants to know or do—and make the first 60 words do the heaviest lifting. Agentic AI and answer engines elevate sources that resolve the task, anticipate follow-ups, and guide next steps.
- Lead with an answer-first summary: a crisp 40–60-word paragraph that states the definition, decision, or outcome up front; this is the text most likely to be quoted or synthesized by AI search.
- Cover follow-ups in sequence: add subheads and bullets for “what it means,” “how to do it,” “compare X vs Y,” and “common pitfalls,” mirroring the conversational turns LLMs propose.
- Include disambiguation and scope notes: explicitly address variants, edge cases, or “it depends” conditions so LLMs can cite you for nuance, not just the headline.
- Provide action affordances: checklists, comparison tables with decisive criteria, calculators, or “next-step” links that agentic systems can surface as actions.
- Document authorship and sources: short evidence blocks with citations and named experts; this bolsters authority signals used by answer engines. Mini‑case: In a controlled SearchPilot-style A/B test for a “compare X vs Y” query, a page rewritten with an answer-first summary, follow-up coverage, and a clear decision matrix outperformed a keyword-stuffed control. Perplexity’s reranking consistently preferred the intent-first variant, citing it in synthesized answers while the control failed to appear.
Semantic Optimization with Entities and Schema
LLMs don’t just read words; they resolve entities and relationships. Your job is to make that resolution effortless.
- Build an entity map: list primary and related entities (people, products, processes), synonyms, and attributes; reflect this map in headings, alt text, and internal links to create a coherent topic graph.
- Use precise terminology with variants: introduce the canonical term and nearby synonyms in context to minimize ambiguity and reduce embedding distance between your page and AI-generated summaries.
- Add schema to expose meaning: implement Article/BlogPosting plus supporting types like HowTo, Product, Review, Organization, Person, and BreadcrumbList to clarify content type and relationships for answer engines.
- Structure modular components: definitions, steps, tables, and FAQs separated with clear labels so LLMs can extract the right component for the right conversational turn.
- Refresh strategically: update claims, examples, and comparisons when the landscape changes; answer engines weight freshness when choosing citations for time-sensitive topics. Why this works: AI Overviews and similar systems check semantic alignment between their synthesized statements and candidate sources. When your content maps entities clearly and signals type with schema, it reduces ambiguity, strengthens authority perception, and increases your odds of being cited inline or beneath the summary.
Experience and Engagement Signals
Engagement is a credibility proxy. If users stay, scroll, copy, and click “next steps,” engines infer your page satisfied intent.
- Engineer interaction for intent: add sticky “Do this next” links, jump links to follow-ups, and collapsible FAQs targeting common clarifications generated by LLMs.
- Optimize readability and retrieval: short paragraphs, scannable subheads, descriptive tables/diagrams, and accessible alt text; these components are easy for users to parse and for answer engines to quote.
- Measure the right micro-conversions: track scroll depth to key components, table interactions, copy-to-clipboard on code or checklists, accordion opens, and outbound clicks from “next steps.”
- Prioritize speed and stability: fast loads, minimal layout shift, and mobile-first spacing to prevent friction during the crucial first second when users decide to bounce or engage.
- Close the loop with iteration: analyze engagement drop-offs and AI SERP appearance; expand sections where users linger, add clarifications where they hesitate, and prune bloat that dilutes the answer. Why this works: when multiple pages are semantically similar, answer engines look to structure and engagement as tie-breakers. Pages that demonstrate real user satisfaction—clear design, meaningful interactions, complete yet concise coverage—are more likely to be selected, surfaced, and clicked from AI summaries.
In practice, these pillars operate as one: intent-first content provides the substance; semantic optimization exposes meaning; experience signals prove value. Together, they form the backbone of modern AI search optimization strategies and the foundation of effective answer engine optimization.
Algorithmic Shifts: What’s Changing in AI Search Engines
[#algorithmic-shifts]
AI search has moved from ranking pages to ranking evidence. Large language models weigh multiple signals to decide which sources to consult, which passages to trust, and how to assemble an answer that satisfies intent and anticipates the next step. Understanding those signals—and how agentic flows extend beyond a single result page—redefines what “visibility” means.
How LLMs select and weigh sources
When an answer engine or AI Overview prepares a response, it draws candidate documents from the organic search index—the same corpus used for traditional rankings. The model then scores and synthesizes, emphasizing:
- Authority and trust: recognizable expert domains, named authors with credentials, transparent sourcing, and original insights. Research-backed references and clear editorial standards strengthen this signal.
- Semantic alignment: embedding similarity between the synthesized statements and specific passages on your page. Clear entity definitions, consistent terminology, and disambiguation reduce embedding distance and improve match quality.
- Freshness and recency: up-to-date facts, updated comparisons, and current examples, especially for topics with fast-moving details. Revision notes and changelogs help the system detect currency.
- Structure and schema presence: explicit components (40–60-word summary, definitions, steps, tables) plus JSON-LD schema (Article, HowTo, FAQPage, Product, Review, Organization, Person) that surface entities and relationships.
- Engagement proxies: signals that users find your content helpful—readability, depth of interaction, low pogo-sticking, and meaningful micro-conversions. When relevance is tied, structured clarity and engagement often tip selection. AI Overviews generate original text rather than quoting a single page, then attribute via inline and/or supporting links. There is no sentence-level citation trail; instead, links represent sources that best support portions of the summary. This is why precision in entities, structure, and evidence matters: it increases your chance of being selected as a supporting source and linked prominently.
LLM answer engines weigh evidence and structure, not just links, to assemble concise, cited answers.
Agentic flows: retrieval, browsing, and planning
Modern answer engines don’t stop at retrieval. They:
- Retrieve-augment: pull in passages from multiple sources, compare claims, and reconcile contradictions before drafting.
- Browse and tool-use: open pages, expand abbreviations, run calculations, or call APIs (e.g., pricing, availability) to verify details or fill gaps.
- Plan multi-step actions: map a user’s intent (decide, then do) into a sequence of steps and present next actions—comparison, configuration, booking, checkout. Implication for “ranking”: instead of a linear list, you’re competing to be chosen at three junctures—evidence inclusion, synthesis influence, and next-action placement. Pages that package decision criteria and actions (tables, calculators, checklists, deep links) can surface not just as sources, but as recommended next steps.
CTR and zero‑click realities
Answer boxes absorb attention and clicks. Some traffic shifts away from traditional position-based listings toward:
- The answer box itself (zero‑click satisfaction)
- Cited sources linked inline or beneath the answer
- Follow-up suggestions and action links While generalized CTR may decline for some queries, being cited can yield high-intent visits because users click through for depth, verification, or to execute the next step. Monitor your analytics accordingly: traffic from AI Overviews is classified as Organic Search in Google Analytics.
AI answers shift clicks toward answer boxes and cited sources, changing how visibility translates into traffic.
Walkthrough: how an LLM ranks a decision query
Decision query: “best project management approach for remote teams”
- Intent resolution The system classifies the primary intent as “decide,” with sub‑intents “compare frameworks,” “highlight trade‑offs,” and “recommend based on team size and sync frequency.” Entities include Scrum, Kanban, Scrumban, OKRs, asynchronous workflows, and remote collaboration tools.
- Candidate selection From the organic index, the engine gathers pages that:
- Define each framework with remote‑work nuances
- Offer a comparison matrix (criteria: ceremony overhead, async suitability, WIP visibility, tooling)
- Include expert commentary and recent examples of distributed teams Authority/trust narrows the pool to consistent, expert sources; semantic alignment favors pages that use the same entities and criteria. Freshness weights articles that address remote and hybrid models explicitly.
- Evidence scoring For each candidate, the model extracts passages and scores:
- Alignment: does the passage map closely (embedding similarity) to the claim “Kanban supports asynchronous work with low ceremony”?
- Structure: is there a clear 40–60-word summary and a table comparing frameworks by remote‑ready criteria?
- Trust signals: named author with domain expertise, citations to recognized sources, and transparent methodology.
- Synthesis The LLM drafts an answer: a concise decision summary, followed by a balanced comparison and a conditional recommendation (e.g., “For teams with overlapping time zones and complex backlogs, Scrum offers cadence clarity; for highly asynchronous teams, Kanban minimizes ceremony and improves flow visibility; Scrumban blends both for evolving roadmaps.”). Ambiguities (“What about OKRs?”) are addressed in follow-ups.
- Link placement Inline links anchor to the strongest supporting passages for each claim (e.g., a Kanban remote-work study; a Scrum cadence guide), with a supporting list of citations beneath the answer. Sources chosen exhibit high semantic match, clear structure/schema, and credible authorship. What made the cut
- A page with a crisp summary, a comparison table keyed to remote‑specific criteria, HowTo/FAQ schema, and expert attribution.
- A research-backed article with case studies and scannable definitions for each framework.
- A tooling guide that translates the decision into actions (board setup checklist), earning a “next step” recommendation.
What missed it
- Keyword-heavy pages listing “best PM methods” without remote-specific entities or structured comparison.
- Outdated write-ups with generic pros/cons and no authorship details.
What to do next
- Expose entities and comparisons explicitly; use schema to label content type and relationships.
- Maintain freshness for decision content; add update notes and current examples.
- Engineer modular components (summaries, tables, steps) that map cleanly to conversational turns.
- Track AI SERP presence, citation frequency, and engagement from Organic Search; iterate where intent isn’t fully satisfied. The takeaway: in AI search, selection is earned through intent clarity, entity precision, structured evidence, and demonstrated usefulness. Optimize for being chosen as evidence, as the synthesized answer’s backbone, and as the logical next step.
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO): Strategies for Featured Answers
[#aeo]
Answer engines surface pages that make answers obvious, nuance explicit, and next steps effortless. AEO is the art of packaging substance so LLMs can quote it, users can trust it, and agentic systems can act on it.
Structuring Pages for Direct Answers and Zero‑Click Search
Use this repeatable template to win featured answers and support zero‑click scenarios while still earning engaged visits.
- 40–60‑word answer summary
- Lead with the definition, decision, or outcome. One sentence per claim. No fluff.
- Definitions and variations
- Clarify terms, synonyms, and entity aliases. State scope and exclusions.
- Steps or comparison
- Show “how to” with numbered steps, or “which is best” with a decisive table and criteria.
- Examples and pitfalls
- Provide concrete examples; list common mistakes and edge cases.
- Evidence and citations
- Attribute claims with sources, authorship, and methodology notes.
- Related FAQs with jump links
- Add 4–6 publisher‑written FAQs; link to anchors on the page.
- Clear next actions
- Offer checklists, calculators, templates, or “start now” links. AEO template: an answer-first page layout that supports featured answers and follow-up queries.
Pro tip: Format each section as a distinct, scannable module. This modularity lets answer engines extract just the piece needed for a specific conversational turn.
Optimizing for Conversational and Agentic Queries
LLMs think in turns. Anticipate and instrument those turns.
- Anticipate follow‑ups
- After your summary, add a “Next questions” box aligned to typical turns: “What does it depend on?”, “How do I do it?”, “What’s the best option for X vs Y?”, “What are common mistakes?”
- Clarify scope and “it depends”
- Use conditional patterns: “If [context], then [recommendation]. If [constraint], then [alternative].” This gives agentic AI safe, nuanced guidance to cite.
- Handle variants and synonyms
- Introduce the canonical entity, then parenthetical variants: “Scrumban (aka Scrum‑Kanban).” Include disambiguation sentences for look‑alike terms.
- Entity disambiguation
- Add a “Related but different” note: “OKRs are goal‑setting, not a delivery framework,” and link to the correct entity page.
- Conversational affordances
- Provide short, quotable definitions, one‑line step labels, and decision criteria with labels that match user phrasing. Use jump links and sticky “Do this next” CTAs. Why it works: Answer engines reward content that resolves the current turn while making the next turn obvious. You become the path of least resistance.
Schema Markup That Reinforces AEO
Use JSON‑LD to make your components machine‑readable. Keep markup truthful to visible content.
- Article with Person/Organization
- Use for editorial content; include author (Person) and publisher (Organization) to strengthen trust.
- FAQPage
- Use for publisher‑written FAQs that appear on the page. Note: rich‑result visibility is largely limited to authoritative government/health sites, but structured FAQs still aid understanding.
- QAPage
- For single‑question pages with user‑generated answers (forums, community Q&A). Do not use for editorial FAQs.
- HowTo
- For step‑by‑step instructions with required properties (steps, names). Add images and time where appropriate.
- Product with Offer + AggregateRating + Review
- For product detail pages; avoid self‑serving reviews. Only mark up reviews you’re allowed to publish.
- Organization and Person
- Express identity, authorship, and publisher details. Add logo and profiles via sameAs.
- Speakable (optional, niche)
- Scope to Article segments intended for voice; typically relevant to news‑style content. Implementation guardrails:
- Only one FAQPage or one QAPage per page.
- Markup must reflect visible, user‑facing content.
- Combining types is allowed when content warrants it (e.g., Article + HowTo + FAQPage).
- Markup does not guarantee rich results.
- Follow Google’s guidelines to avoid misuse and manual actions.
Validation and monitoring:
- Test with Google’s Rich Results Test before publishing.
- Monitor enhancements, errors, and warnings in Search Console.
- Update schema whenever on‑page content changes; keep identity (Organization/Person) consistent across pages.
JSON‑LD: Concise, Valid Examples
Article (with author and organization)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "Article","headline": "Example Article","description": "A concise summary of the page topic.","image": "https://example.com/cover.jpg","author": {"@type": "Person","name": "Alex Writer","url": "https://example.com/authors/alex-writer"},"publisher": {"@type": "Organization","name": "Example Co","logo": {"@type": "ImageObject","url": "https://example.com/logo.png"}}}
FAQPage (publisher‑written FAQs on the page)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "FAQPage","mainEntity": [{"@type": "Question","name": "What is AEO?","acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Answer Engine Optimization is structuring content for direct answers and conversational queries." }},{"@type": "Question","name": "Why add schema?","acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Schema exposes entities and content types to search engines and answer systems." }}]}
QAPage (single user question with answers)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "QAPage","mainEntity": {"@type": "Question","name": "How do I reset my password?","acceptedAnswer": { "@type": "Answer", "text": "Select 'Forgot password' on the login page and follow the emailed instructions." }}}
HowTo (step‑by‑step instruction)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "HowTo","name": "How to audit AEO on a page","description": "A quick checklist to validate answer-first content.","step": [{ "@type": "HowToStep", "name": "Add summary", "text": "Write a 40–60-word answer at the top." },{ "@type": "HowToStep", "name": "Define scope", "text": "Clarify terms, variants, and exclusions." }]}
Product with Offer, AggregateRating, and Review (avoid self‑serving)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "Product","name": "Widget One","image": "https://example.com/widget.jpg","description": "A concise product overview.","sku": "W1","brand": { "@type": "Brand", "name": "BrandCo" },"offers": {"@type": "Offer","url": "https://example.com/widget-one","priceCurrency": "USD","price": "19.99","availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"},"aggregateRating": { "@type": "AggregateRating", "ratingValue": "4.6", "reviewCount": "37" },"review": [{"@type": "Review","author": { "@type": "Person", "name": "Jamie" },"reviewRating": { "@type": "Rating", "ratingValue": "5", "bestRating": "5" },"reviewBody": "Clear instructions and solid build quality."}]}
Organization
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "Organization","name": "Example Co","url": "https://example.com","logo": "https://example.com/logo.png","sameAs": ["https://www.linkedin.com/company/example"]}
Person
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "Person","name": "Alex Writer","url": "https://example.com/authors/alex-writer","jobTitle": "Editor","worksFor": { "@type": "Organization", "name": "Example Co" },"sameAs": ["https://twitter.com/alexwriter"]}
Speakable (optional, niche; scoped to Article)
{"@context": "https://schema.org","@type": "Article","headline": "Example Article","speakable": { "@type": "SpeakableSpecification", "cssSelector": [".speakable"] }}
Bottom line: AEO is clarity engineered—short, certain, and structured. Give answer engines a precise summary to quote, the nuance to trust, the schema to parse, and the actions to propose. Then validate, monitor, and iterate as conversational demand evolves.
Maximizing Click-Through Rates in AI Search Results
[#ctr]
AI answers satisfy intent in the SERP; engineered snippets earn the click. In AI search, the highest-CTR results align three layers: a task-first title that promises value, a 40–60‑word answer summary that resolves the core question, and metadata plus visuals that make your result scannable, credible, and action-oriented.
High-CTR snippets combine task-first titles, concise summaries, visuals, and trust signals with clear next steps.
Engineer meta and on‑page answer snippets for AI SERPs
- Title formula (task-first, entity-anchored, benefit-forward) Pattern: [Verb to complete task] + [Target entity/topic] + [Outcome/benefit] Examples:
- Optimize for AI Search Engines: Structure Answer‑First Pages That Earn Clicks
- Compare Kanban vs Scrum: Choose the Right Framework for Remote Teams
- Implement Schema Markup: Expose Entities and Win Answer Visibility
- Answer summary (40–60 words; first 160 characters do the most work) Guidance:
- Lead with a direct answer, then qualify with the most important condition or “it depends.”
- Use one sentence per claim; avoid throat-clearing or brand intros.
- Front-load decisive phrases and entities so the first 160 characters read as a complete, credible mini‑answer.
- Meta description pattern (outcome, evidence, next action; aligned to OG/Twitter) Structure: [Outcome] + [Proof/evidence element] + [Next action] Example: Increase click-through rate in AI-powered SERPs by pairing answer-ready summaries with schema and modular visuals. Includes before/after templates, KPIs, and a checklist—use jump links to apply it now.
- OG/Twitter alignment (express as a metadata spec, not HTML)
{
"og:title": "Optimize for AI Search Engines: Earn Answers and Clicks",
"og:description": "Answer-ready summaries, schema cues, and modular visuals to lift CTR. Includes templates, KPIs, and a test-and-learn loop.",
"og:image": "/images/high-ctr-ai-result-anatomy.png",
"twitter:card": "summary_large_image"
}
- Breadcrumbs and on‑page anchors
- Use descriptive breadcrumbs (e.g., Home › Blog › AI Search › CTR Tactics). These can appear in snippets and guide users to context.
- Add jump links to key modules (e.g., #summary, #comparison, #faq). These anchors often surface as sitelinks in SERPs and inside AI answers.
- Optional: implement BreadcrumbList schema to make the trail machine‑readable.
Before/after: snippet optimization example
Topic: “How to optimize for AI search engines”
Original
- Title: AI Search Optimization: Tips and Tricks
- 40–60‑word summary: AI search is changing SEO. This article covers various AI search optimization strategies and explains how businesses can improve results using these approaches.
- Meta description: Learn about AI search optimization and improve your SEO with helpful tips and insights.
Improved (title formula + decisive summary + outcome/evidence/next action)
- Title: Optimize for AI Search Engines: Build Intent‑First Pages That Earn Answers and Clicks
- 40–60‑word summary: To optimize for AI search engines, lead with a 40–60‑word answer summary, map entities with schema, and package quotable modules (tables, steps, definitions). Add evidence, author credentials, and next‑step links. This structure increases selection as a cited source and lifts click‑through to deeper guidance.
- Meta description: Lift click-through rate in AI SERPs with answer-first summaries, entity-aware schema, and modular visuals. Includes a proven page template, KPIs to track, and a step‑by‑step iteration loop to sustain gains.
Why the “after” wins
- Task-first title clarifies the action and benefit.
- The summary answers directly, names concrete components (schema, tables, steps), and promises outcomes (citation, CTR lift).
- Meta description uses an outcome → proof → action pattern to invite purposeful clicks.
KPIs to track and how to instrument them
Measurable KPIs
- Click-through rate (CTR): Google Search Console → Performance → Search results → filter target queries/pages.
- Scroll depth to the answer summary: percentage of users reaching the summary module.
- Interaction rate on “next‑step” links: clicks on checklists, templates, calculators.
- Time on page to first interaction: average seconds until first jump‑link, accordion, or copy action.
Instrumentation
- Event tracking (names and properties):
- jump_link_click: { anchor_id, section_label }
- copy_to_clipboard: { component_type: “summary|code|checklist”, length }
- table_interaction: { action: “sort|filter|download”, table_id }
- accordion_toggle: { section: “FAQ|pitfalls|definitions”, state: “open|close” }
- next_step_click: { link_label: “template|calculator|compare”, destination: “internal|external” }
- Analyze against Organic Search landings:
- Segment by Default Channel Grouping = Organic Search.
- Map event flows for AI-impacted queries; correlate interaction upticks with observed AI SERP presence from monitoring tools.
- Compare “cited” query cohorts vs. non‑cited cohorts to isolate AI Overview influence.
- Note: Traffic from AI Overviews/AI Mode is classified as Organic Search. Treat cited visits as high-intent and evaluate depth of interaction accordingly.
Use visuals and rich media strategically
- Quotable components earn attention:
- Comparison tables with decisive criteria and clear headers
- Diagrams that summarize process or architecture in one frame
- Short code blocks or checklists with copy buttons
- Visual accessibility:
- Alt text describes function and entities (“Comparison table of Kanban vs Scrum by async suitability”).
- Captions state the takeaway in one sentence.
- Avoid dense text in images; rely on labels and legends.
- OG image best practices:
- High-contrast, minimal text, clear title and sub-labels, brand mark unobtrusive.
- Page-unique imagery; reflect the page’s primary entity and task.
- Why LLMs prefer modular visuals:
- Clear labels, legends, and section titles improve extraction and citation.
- Modular components map to conversational turns (define, compare, decide), increasing selection as inline evidence.
10‑point CTR checklist for AI‑powered SERPs
- Task-first, benefit-forward titles with explicit entities.
- 40–60‑word answer summary above the fold; first 160 chars decisive.
- Schema cues (Article + Organization/Person; BreadcrumbList optional) for context.
- Jump links to core modules; anchors named with user phrasing.
- Modular visuals (tables, diagrams) with descriptive alt text and captions.
- Internal “next‑step” CTAs aligned to intent (template, calculator, comparison).
- Author and organization trust signals near the summary (credentials, methodology).
- Mobile readiness: short paragraphs, tap‑targets, no layout shift.
- Load speed: prioritize summary, table, and hero visual; defer non‑critical scripts.
- Clear affordances to act: copy buttons, downloadable assets, and persistent “Do this next” links.
Measurement and iteration
- Correlate: Track Organic Search landings and overlay AI SERP presence from monitoring tools. Expect higher interaction quality when cited in AI answers even if total clicks are lower.
- Test-and-learn loop:
- Baseline: capture CTR, scroll-to-summary %, and first-interaction time for target pages.
- Snippet engineering: revise title, summary, meta, and OG; add anchors and modular visuals.
- Publish: validate schema; ensure breadcrumbs resolve and anchors render.
- Measure: compare KPIs in Organic Search; segment by query groups with AI answer presence.
- Iterate: keep what lifts CTR and interaction rates; refine summaries that underperform; expand or tighten visuals as needed. When zero‑click answers rise, clicks concentrate where clarity and credibility converge. Engineer the snippet, surface the substance, and make the next step unmistakable—that’s how AI Search Optimization Strategies convert visibility into visits and visits into value.
Adapting Your Workflow for AI Search Optimization
Winning answers isn’t luck—it’s a disciplined loop of intent mapping, schema-first publishing, and relentless iteration. Operationalize the principles above with a lightweight, repeatable workflow your team can run at scale.
A repeatable workflow aligns teams around intent-first planning, schema, and continuous iteration.
The AI Search Optimization Workflow (10 steps)
- Topic research Deliverables: topic clusters, entity inventory, AI SERP snapshot, opportunity notes. Owner: SEO Strategist. Tools: SERP intelligence, entity extraction, AI answer presence monitors.
- Intent mapping Deliverables: task-oriented intent map (primary + sub-intents, follow-ups, micro-actions). Owner: Content Strategist. Tools: SERP feature analyzers, query classification, Search Console.
- Answer-first outline Deliverables: 40–60-word summary, modular outline (definitions, steps/table, pitfalls, evidence, FAQs), visual plan. Owner: Managing Editor. Tools: outlining/briefing assistants, diagram/table authoring.
- AEO page structuring Deliverables: page draft with modules, jump-link anchors, internal linking to entity hubs, next-step CTAs. Owner: UX Writer/Content Designer. Tools: CMS with components, accessibility linters.
- Schema implementation Deliverables: JSON-LD (Article + Organization/Person; add HowTo, FAQPage, Product, Review, BreadcrumbList as needed), validation logs. Owner: Technical SEO. Tools: schema generators/linters, Google Rich Results Test, Search Console.
- Snippet engineering Deliverables: titles, meta descriptions, OG/Twitter, polished 40–60-word on-page summary, breadcrumb labels, anchors. Owner: SEO Editor. Tools: SERP previewers, snippet scorers, social card debuggers.
- QA & accessibility Deliverables: link checks, a11y audit, performance report (Core Web Vitals), schema re-validation. Owner: QA Analyst. Tools: performance auditing, accessibility testing suites, link/HTML validators.
- Publish Deliverables: indexable live URL, updated sitemap, URL Inspection request, analytics events installed. Owner: Web Manager. Tools: CMS release flow, Search Console, tag manager, crawler tests.
- Monitor AI SERP and citations Deliverables: dashboard for AI answer presence, citation capture (inline/supporting), screenshots, alerts; Organic Search correlation. Owner: SEO Analyst. Tools: AI SERP monitors, Search Console, analytics, session replay.
- Iterate Deliverables: hypothesis backlog, experiments (snippet/layout/schema), versioned updates, readouts. Owner: Growth/SEO Lead. Tools: experimentation, content version control, coverage/scoring tools.
A neutral toolstack by capability
- AI SERP and citation monitoring Capabilities: detect AI answer presence by query, parse cited domains/URLs, track inline vs. supporting links, screenshot/change history, alerts.
- Entity mapping and knowledge graphing Capabilities: extract/disambiguate entities, build ontologies, visualize relationships, export structured data recommendations.
- Schema creation and validation Capabilities: JSON-LD authoring at module level, linting, batch validation; verify with Google Rich Results Test; monitor Enhancements in Search Console.
- Content scoring and readability Capabilities: task clarity checks, reading-level guidance, terminology consistency, coverage completeness vs. intent map.
- User research Capabilities: on-site surveys, moderated interviews, session replay/heatmaps for task completion diagnostics.
- Analytics and log analysis Capabilities: GA4 event modeling and segmentation, Organic Search cohorting, server log inspection for bot/crawl diagnostics.
- Change monitoring and version control Capabilities: content diffing, approvals, rollback, release tagging, schema block comparisons.
- Tag management Capabilities: data layer orchestration, consent gating, event QA (Preview/Debug), performance-friendly triggers.
- Google platform essentials
- Search Console for indexing, Performance, Enhancements
- GA4 for Organic Search segmentation and event analysis
- Tag manager for event deployment and debugging
Engagement instrumentation (how to measure what matters)
Event taxonomy (final):
- jump_link_click: anchor_id, section_label, source_context
- copy_to_clipboard: component_type (summary|checklist|code|citation), content_length
- table_interaction: table_id, action (sort|filter|download|paginate), column/direction/filter_value (when applicable)
- accordion_toggle: section (faq|pitfalls|definitions|appendix), item_id, state (open|close)
- next_step_click: link_label (template|calculator|compare|demo|download), destination (internal|external)
Implementation:
- Deploy via tag manager; push concise parameters to the data layer; respect consent; debounce rapid repeats.
- Map to GA4 custom events/parameters; export to BigQuery if warehouse joins are needed.
Segmentation:
- Isolate Organic Search (GA4 default channel grouping).
- Join Search Console (page, query, clicks, impressions) with AI SERP monitoring labels (ai_answer_present, citation_status).
- Build cohorts: no AI answer, AI answer not cited, cited (support), cited (inline). Compare interaction rates and next-step CTR by cohort.
AI Search Readiness checklist (Yes/No)
- Intent map complete (primary, sub-intents, 6+ follow-ups, micro-actions defined).
- 40–60-word answer summary above the fold in plain HTML.
- Entity coverage and disambiguation handled; internal links to entity hubs present.
- Internal anchors/jump links implemented and usable as sitelinks.
- Schema validated: Article + Organization/Person; add HowTo/FAQPage/Product/Review/BreadcrumbList as warranted (Rich Results Test clean).
- Visuals include descriptive alt text and one-line captions; key decision visual present.
- Author and organization trust signals visible near the summary.
- Mobile readability (short paragraphs, clear hierarchy, tappable targets) verified.
- Performance budget respected (Core Web Vitals passing; defer noncritical scripts).
- Monitoring configured for AI SERP features, citation capture, and alerts; baselines recorded.
- Governance in place (RACI owners, approval gates documented).
- Revision cadence and versioning documented (changelog, rollback SOP).
Governance and cadence
- Owners and gates Accountable owners per step (Strategist, Editor, Tech SEO, QA, Web Manager, Analyst). Hard gates: intent map approved, outline approved, schema valid, a11y/performance passed, monitoring live.
- Pre-publish checks Answer summary quality; modular structure with anchors; truthful schema; a11y verified; performance passing; analytics events firing; Search Console fetch successful.
- Versioning and rollback Use a Git-like model: draft branches, two-person approvals (content + schema), tagged releases, diffs for summaries/anchors/schema blocks; rollback on breakage or material CTR regressions.
- Merge, split, retire criteria Merge when entity overlap and cannibalization dilute engagement; split when multi-intent sprawl suppresses interaction or agentic flows diverge; retire when redundant, non-compliant, or persistently underperforming after iteration. Always 301 appropriately, merge schema, update sitemaps, and revalidate.
- Cadence Daily: monitor citations/AI presence and critical errors. Weekly: cross-functional standup and snippet/schema spot-checks. Monthly: cohort review (cited vs. non-cited), experiment decisions. Quarterly: entity coverage audit, architecture refresh, standards update. Put simply: make the work a loop, not a leap. When intent is mapped, structure is modular, schema is truthful, and measurement is meticulous, AI search becomes predictable—and your visibility becomes durable.
Future Trends: Preparing for the Next Wave of AI Search
[#future-trends]
The center of gravity is shifting from ranking answers to orchestrating outcomes. As agentic AI matures inside search, the systems that previously summarized will increasingly plan, verify, and execute. Your advantage comes from designing content and components that can be selected as evidence, assembled as guidance, and invoked as actions.
Agentic AI: from answers to actions
Agentic AI doesn’t just retrieve; it reasons, tools, and transacts.
- Multi-step planning: Given a goal, agents decompose it into sub-tasks (research, compare, decide, act), refreshing context with each turn.
- Tool and browse use: Agents open pages, follow links, check availability, run calculations, and query APIs to verify claims and fill gaps.
- Assisted transactions: Within the search flow, agents pre-configure carts, schedule appointments, or generate drafts—then hand control to the user for confirmation. What this demands:
- Provide “action surfaces”: clear next-step links, deep links with parameters, downloadable templates, calculators, and structured prompts.
- Publish decision primitives: comparison criteria, thresholds, and conditional rules that an agent can map into planning steps.
- Keep claims verifiable: short, citable statements with nearby evidence and authorship—agents will privilege sources that are easy to audit.
Interfaces and behavior: conversational, cited, and increasingly zero‑click
Search is becoming a dialogue. Users ask, refine, and delegate; engines reply with generated summaries paired with inline and supporting links, selected from the organic index by authority, semantic alignment, freshness, and structure. Expect:
- Conversational UIs: Follow-up prompts are integral. Your content should anticipate them and expose answers as modular components.
- Inline citations/links: Sources are visible inside the answer and beneath it; clarity, entity precision, and concise summaries raise the odds of being cited.
- Zero-click and assisted actions: Many sessions complete without a traditional click. When clicks do occur, they’re purposeful—verification, depth, or execution. Engineer for all three. Optimization implications:
- Keep the 40–60-word answer at the top; it’s the most quotable unit.
- Surround claims with definitions, comparisons, and evidence modules that map cleanly to follow-up turns.
- Treat “next steps” as first-class content—agents surface them as suggested actions.
Multimodality: text, image, video, and voice
Queries and answers are no longer text-only. Users point a camera at a part, paste a screenshot of an error, or ask by voice; engines respond with annotated images, short clips, or spoken summaries.
Make your content multimodal-ready:
- Images and diagrams: Add labels and callouts; use descriptive filenames and alt text that name entities and relationships. Pair each visual with a one-line caption that states the takeaway.
- Video: Provide structured chapters, on-screen labels, and full transcripts. Summarize key steps in text nearby so LLMs can quote without parsing long media.
- Voice: Prioritize concise definitions and scannable steps. Consider speakable segments for news-like content; keep the visible text aligned to what you want spoken.
Why it works: Multimodal agents extract meaning from labels, captions, and transcripts. When your assets are semantically consistent—terms, entities, and steps aligned—selection improves across formats.
How to future‑proof your strategy
Shift from pages to portable parts, and from static articles to verifiable, actionable components.
- Content‑as‑components
- Design reusable modules: summary, definition, decision table, steps, pitfalls, evidence. Version each module; maintain a changelog.
- Action surfaces and APIs
- Provide deep links with parameters, embeddable calculators, and lightweight APIs where appropriate. Document inputs/outputs so agents can compose actions safely.
- Knowledge graphs and entity hubs
- Build hub pages for core entities with consistent definitions, attributes, synonyms, and cross-links. Mirror this structure in schema to reduce ambiguity in selection.
- Freshness and provenance signals
- Timestamp updates, note what changed, and place citations near claims. Explicit provenance helps agents prefer your material when verifying.
- Governance standards
- Institutionalize an approval path for summaries, definitions, and schema blocks. Enforce a schema QA gate, a performance/a11y gate, and a measurement gate before publish. Maintain author credentials and organizational identity consistently across content. The arc of AI search moves from retrieval to action; optimize content components and affordances at every stage.
Expert prediction: Agentic AI will shift search from “find and decide” to “decide and do,” with engines assembling plans, validating sources, and initiating tasks by default. Sites that expose clean components and safe action surfaces will be chosen as both the proof and the path.
What stays true as search evolves
- Selection signals remain steady: authority, semantic alignment, freshness, structure, and engagement decide which sources support generated summaries and earn inline/supporting links.
- Organic index sourcing persists: even as answers are generated, the pool of candidates is drawn from organic search; your job is to be the clearest, most verifiable match.
- Measurement matters more: zero-click is not zero value—track citation presence, assisted actions, and post-click depth to see the whole impact.
Closing the loop: key takeaways
- Run the workflow: intent map → answer-first outline → AEO structure → schema validation → snippet engineering → publish → monitor → iterate.
- Package for answers: 40–60-word summaries, definitions, steps, comparisons, evidence, and next-step components—modular, quotable, and verifiable.
- Mark up meaning: truthful, validated JSON-LD (Article, HowTo, FAQPage, Product, Review, Organization, Person, BreadcrumbList) that reflects visible content.
- Measure and improve: monitor AI SERP presence and citations, instrument engagement events, and iterate based on gaps in selection, clarity, and actionability. AI Search Optimization Strategies are durable when they are disciplined: design components that answer, prove, and enable action; validate schema; and keep the measurement loop tight. Do this consistently, and you won’t just survive the next wave of AI search—you’ll be the current it rides.
FAQs
[#faqs]
How do you optimize for AI search engines versus traditional SEO?
Prioritize intent-first, answer-ready content with clear entities, concise 40–60-word summaries, modular sections (definitions, steps, tables), and truthful schema. Traditional SEO emphasizes rankings and keywords; AI search rewards clarity, structure, and engagement that support synthesis and actions. Measure citation presence and next-step clicks, not just positions. (See Understanding AI Search #understanding-ai-search)
What is Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) and why does it matter?
AEO structures pages so answer engines can quote a precise summary, trust your nuance, and propose your actions. It packages answers, evidence, and next steps in modules that map to conversational turns, improving citation odds and high-intent clicks even in zero-click SERPs. (See Answer Engine Optimization #aeo)
How can I improve click-through rate in AI-powered SERPs?
Engineer snippets: task-first titles, a decisive 40–60-word answer summary, schema-rich breadcrumbs, and visual modules that promise depth (tables, diagrams). Add credible authorship near the summary and clear “next-step” links. Track CTR, scroll-to-summary, and interaction events to iterate. (See Maximizing Click-Through Rates #ctr)
Which schema types matter most for AI search and topical authority?
Lead with Article plus Organization and Person to establish identity and authorship. Add HowTo for steps, FAQPage for publisher-written FAQs on-page, Product with Offer/Review for PDPs, and BreadcrumbList for context. Truthful, consistent schema reinforces entity alignment and topical authority signals. (See Answer Engine Optimization #aeo)
FAQPage vs QAPage: what’s the difference and when to use each?
FAQPage is for publisher-written questions and answers displayed on the page; QAPage is for a single user question with multiple user-generated answers (forums). Rich-result visibility for FAQs is limited; use markup only when content matches the schema’s intent and is visible. (See Answer Engine Optimization #aeo)
How do AI Overviews and answer engines choose sources, and how can I be cited?
They select sources by authority, semantic alignment to synthesized claims, freshness, and clear structure/schema; the summary text is generated, with sources linked inline or below. Earn citations by providing precise, verifiable statements, clean entities, and modular evidence near claims. (See Algorithmic Shifts #algorithmic-shifts)
How can I monitor AI SERP/AI Overview presence and citations?
Track AI answer presence by query, capture screenshots, and log cited domains/URLs and link placement (inline vs. supporting). Correlate with Organic Search traffic in analytics and Search Console. Build cohorts (cited vs. non-cited) to compare engagement and iterate content. (See Adapting Your Workflow #adapting-your-workflow-for-ai-search-optimization)
How should I structure answer-first pages for zero-click and featured answers?
Lead with a 40–60-word summary, then definitions, steps or a comparison table, examples, pitfalls, evidence, and related FAQs with jump links. Add clear next actions (templates, calculators) and truthful schema. This modular template maps cleanly to conversational turns. (See Answer Engine Optimization #aeo)
How do I measure engagement and iterate effectively?
Instrument events for jump-link clicks, copy-to-clipboard, table interactions, accordions, and next-step clicks. Track CTR, scroll-to-summary, first-interaction time, and depth. Segment by AI citation cohorts to see lift. Use findings to refine summaries, visuals, and schema. (See Maximizing Click-Through Rates #ctr)
How does agentic AI change content requirements and next-action design?
Design for assistance, not just answers. Provide decision tables, conditional guidance, deep links, calculators, templates, and API endpoints where appropriate. Keep claims short and verifiable with nearby evidence and authorship to earn selection as both proof and action. (See Future Trends #future-trends)
How do I validate and maintain schema without risking misuse?
Use JSON-LD that mirrors visible content. Validate with Google’s Rich Results Test before publishing and monitor Enhancements in Search Console. Update schema alongside content changes; keep Organization/Person identity consistent and avoid self-serving or misleading markup. (See Answer Engine Optimization #aeo)
Schema scope: Implement FAQPage only when the Q&A appears on the page; rich-result visibility for FAQs is largely limited to authoritative government/health sites; use QAPage only for single-question UGC pages; markup must reflect visible content; validate with Google’s Rich Results Test and monitor in Search Console.